A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) on Windows Server 2025
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) on Windows Server 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) on Windows Server 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) on Windows Server 2025

Introduction
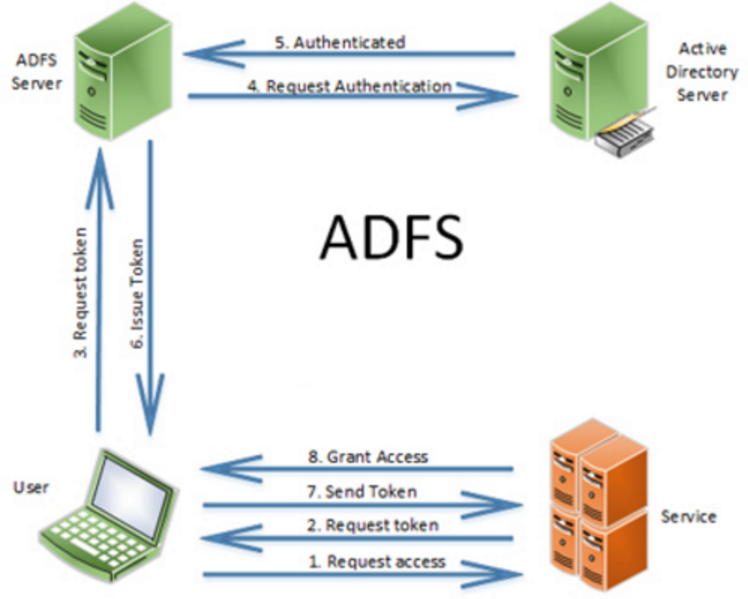
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) plays a pivotal role in securing and managing access to web applications and resources within an organization. It acts as a trusted intermediary, enabling users to access these resources without requiring individual accounts on every system. This guide provides a detailed walkthrough of setting up AD FS on Windows Server 2025, focusing on the crucial steps and configurations necessary for a robust and secure implementation.
Understanding AD FS and its Benefits
AD FS is a key component of Microsoft’s Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution. It utilizes a standard protocol known as Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) to exchange authentication and authorization information between different entities. This allows users to access applications and resources hosted on different platforms and domains, while maintaining a centralized control over access management.
Here are some of the key benefits of using AD FS:
- Simplified Access Management: AD FS centralizes user authentication and authorization, reducing the need for managing multiple accounts across different systems.
- Enhanced Security: AD FS leverages robust security mechanisms like encryption and digital signatures to protect user credentials and sensitive data during authentication and authorization processes.
- Seamless Integration: AD FS integrates seamlessly with Active Directory, leveraging existing user accounts and group policies for streamlined management.
- Improved Compliance: AD FS supports industry standards like SAML and OpenID Connect, facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements for data privacy and security.
- Flexibility and Scalability: AD FS can be deployed in various configurations, including single-server and farm deployments, to accommodate diverse organizational needs and scale according to the number of users and applications.
Setting Up AD FS on Windows Server 2025
The setup process for AD FS on Windows Server 2025 involves several crucial steps, ensuring a secure and functional environment for user access and application integration.
1. Prerequisites:
- Windows Server 2025: Ensure that the server has a valid Windows Server 2025 license and is properly configured for network connectivity.
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS): AD FS requires an existing AD DS environment for user management and group policies.
- Certificate: A valid SSL/TLS certificate is required for securing the AD FS service and communication with relying parties.
- Database: AD FS utilizes a database for storing configuration data. By default, it uses Windows Internal Database (WID), but you can also configure it to use SQL Server.
2. Installing AD FS:
- Open Server Manager: Launch Server Manager on the designated server.
- Add Roles and Features: Navigate to "Add Roles and Features" and select the "Active Directory Federation Services" role.
- Select Role Services: Choose the necessary AD FS role services, including the "Federation Service" and any other required components.
- Installation Confirmation: Review the installation summary and confirm the installation process.
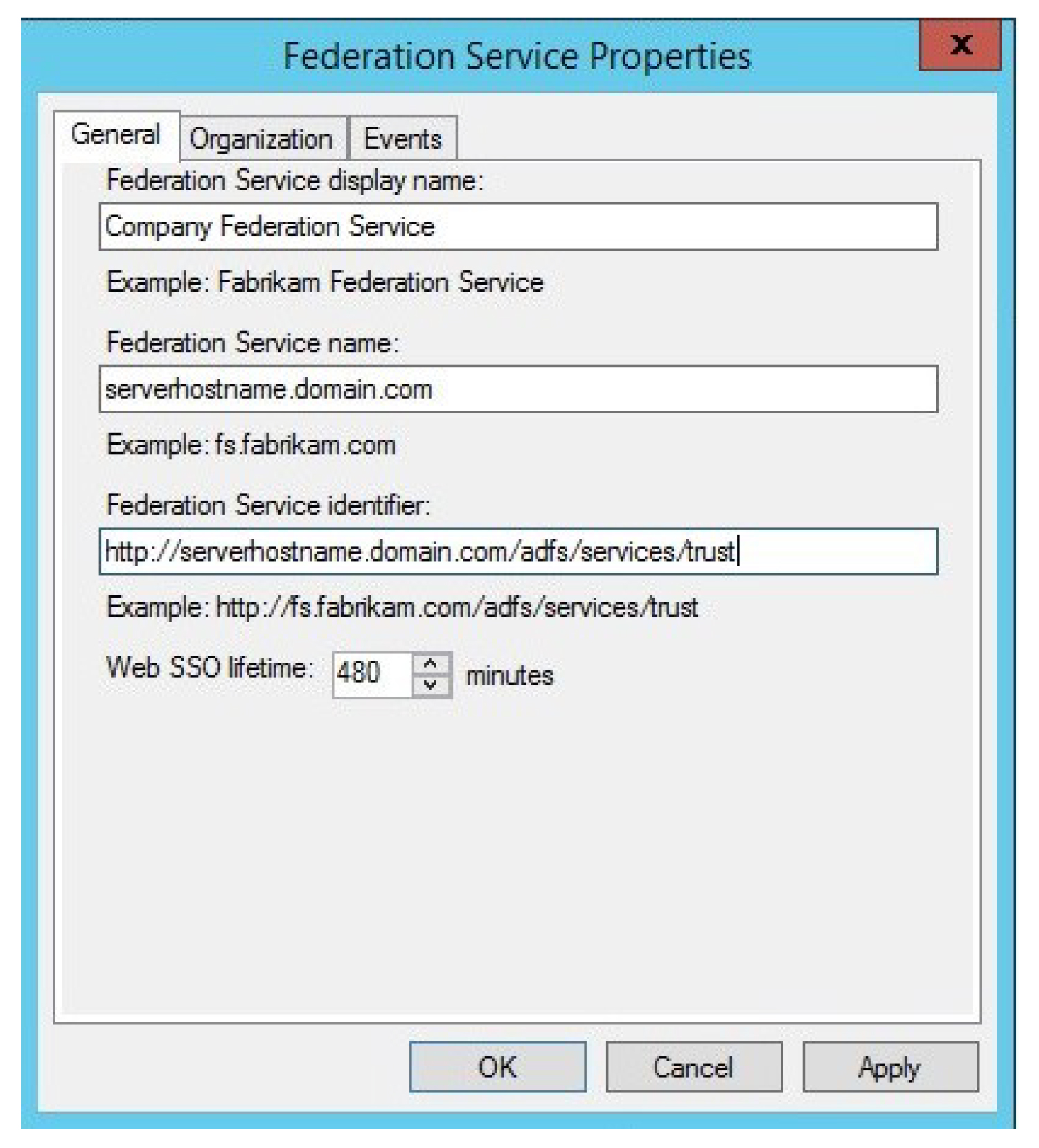
- Post-Installation Configuration: Once the installation completes, configure the necessary settings, including the Federation Service name, the certificate, and the database connection.
3. Configuring AD FS:
- Open AD FS Management: Access the AD FS management console, typically located in the Administrative Tools folder.
- Create Relying Party Trusts: Define the applications or services that will rely on AD FS for authentication. This involves configuring the relying party trust, specifying the SAML metadata and the authentication methods.
- Configure Claims Rules: Define the claims that will be issued to users upon successful authentication. These claims determine the user’s attributes and permissions for accessing resources.
- Manage User Accounts: Ensure that user accounts in the AD DS environment are properly configured and have the necessary permissions for accessing applications and resources.
- Test and Monitor: Conduct thorough testing of the AD FS setup to ensure it meets the organization’s security and access requirements. Implement monitoring tools to track the performance and security of the service.
4. Integrating Applications with AD FS:
- Configure Relying Party Applications: Configure the applications or services that will rely on AD FS for authentication. This typically involves providing the AD FS metadata to the application and configuring the application to trust the AD FS service.
- Configure Claims Mapping: Map the claims issued by AD FS to the attributes required by the relying party application. This ensures that the application receives the necessary information to identify and authorize the user.
- Test Application Integration: Test the integration of the applications with AD FS to ensure users can successfully access and utilize the applications.
5. Advanced Configurations and Security:
- Federation Server Farm: For larger organizations with high user traffic, consider deploying an AD FS farm with multiple federation servers for load balancing and high availability.
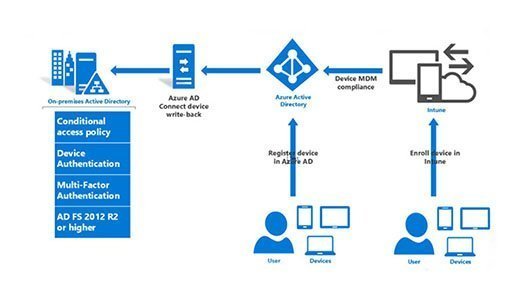
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to enhance security by requiring users to provide additional authentication factors beyond their password, such as a one-time code or biometrics.
- Custom Claims Rules: Develop custom claims rules to tailor the authentication and authorization process based on specific organizational requirements.
- Security Auditing: Configure auditing features to track user activities, authentication attempts, and other security-related events.
- Regular Security Updates: Ensure that the AD FS server and all related components are updated regularly with the latest security patches and updates to mitigate vulnerabilities.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between AD FS and Azure AD?
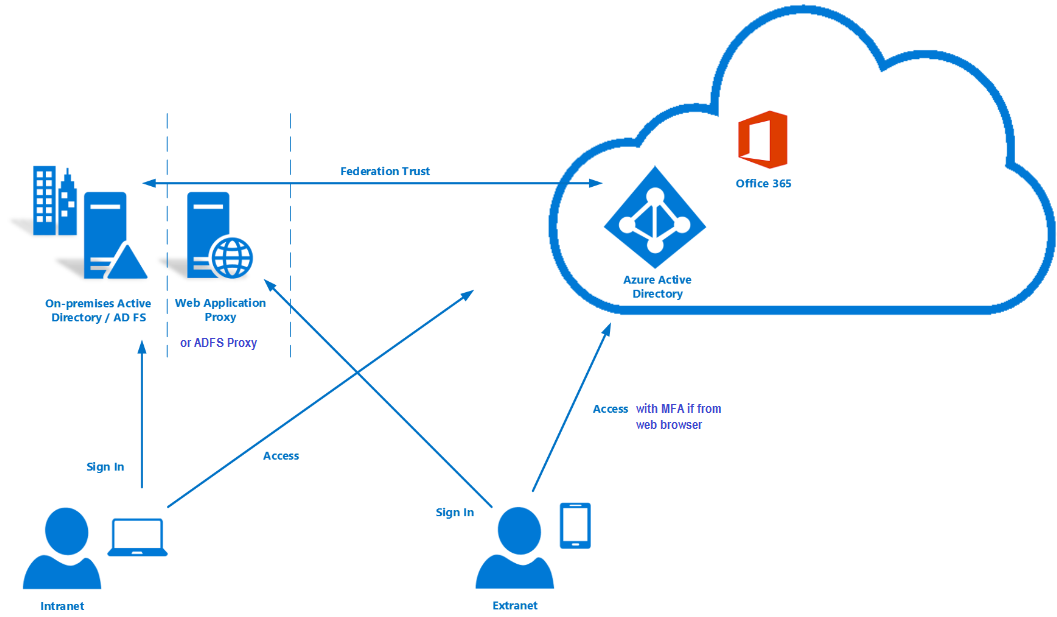
A: While both AD FS and Azure AD provide identity and access management solutions, they serve different purposes and cater to different scenarios. AD FS is primarily designed for on-premises environments, while Azure AD is a cloud-based solution. Azure AD offers a more comprehensive set of features, including single sign-on (SSO) for cloud applications, identity management for hybrid environments, and advanced security features.
Q: Can I use AD FS with cloud applications?
A: Yes, AD FS can be used with cloud applications that support SAML or OpenID Connect protocols. You can configure AD FS to act as an identity provider (IdP) for these applications, enabling users to access them using their existing on-premises credentials.
Q: How do I manage user accounts in AD FS?
A: AD FS relies on Active Directory for user account management. You manage user accounts, groups, and permissions within the AD DS environment. These configurations will be reflected in AD FS, enabling it to authenticate and authorize users based on their AD DS roles and permissions.
Q: What are some best practices for securing AD FS?
A:
- Use Strong Passwords: Enforce strong password policies for all user accounts, including the AD FS service account.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security to user authentication.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep the AD FS server and all related components updated with the latest security patches and updates.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate the AD FS server from other critical systems to limit potential attack vectors.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Tips for Effective AD FS Setup:
- Plan Your Deployment: Carefully plan the deployment of AD FS, considering the organization’s specific needs, security requirements, and integration with existing systems.
- Test Thoroughly: Conduct thorough testing of the AD FS setup before deploying it in a production environment. This ensures that all configurations are working correctly and that users can access the applications and resources as intended.
- Document Your Configuration: Document all configuration changes and settings to facilitate troubleshooting and future maintenance.
- Stay Updated: Stay informed about the latest security updates, best practices, and new features for AD FS to ensure a secure and efficient environment.
Conclusion
Implementing AD FS on Windows Server 2025 provides a robust and secure solution for managing user access to web applications and resources within an organization. By centralizing authentication and authorization, leveraging existing Active Directory infrastructure, and integrating with various applications and services, AD FS simplifies access management, enhances security, and improves compliance with industry standards. By following the steps outlined in this guide and implementing best practices for security and maintenance, organizations can leverage the full potential of AD FS to secure their digital assets and empower users with seamless access to critical resources.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) on Windows Server 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
