A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals
- 3.2 Benefits of Storage Spaces
- 3.3 Implementation and Configuration
- 3.4 Storage Spaces Direct
- 3.5 Best Practices for Storage Spaces
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server

Storage Spaces, a powerful feature introduced in Windows Server 2012, provides a flexible and efficient way to manage storage resources. It allows administrators to create virtualized storage pools from physical disks, enabling various configurations tailored to specific workloads. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of Storage Spaces, delving into its functionalities, benefits, and best practices.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, Storage Spaces in Windows Server acts as a software-defined storage solution, enabling the pooling of physical disks to create a virtualized storage space. This space can then be divided into logical volumes, resembling traditional hard drives, for hosting applications and data. The key advantage lies in its flexibility, allowing for diverse configurations to suit various needs, including:
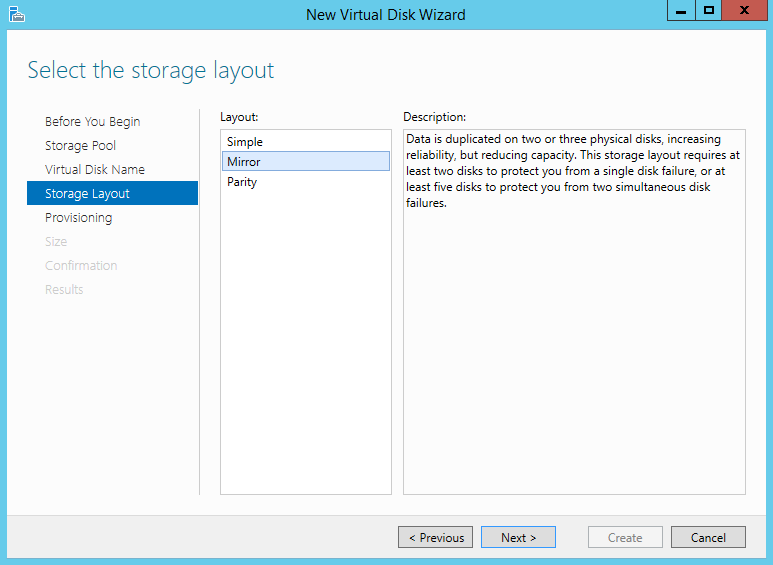
- Simple Storage: This configuration provides a straightforward approach to pooling disks, creating a single, larger storage space. Ideal for general-purpose storage needs, it offers simplicity and ease of management.
- Mirrored Storage: Providing redundancy, this configuration replicates data across two or more disks. In case of a disk failure, the remaining disks ensure data availability and prevent data loss. This is particularly beneficial for critical applications and systems.
- Parity Storage: This configuration offers a balance between performance and redundancy. It utilizes parity data to reconstruct lost data in case of disk failure. This configuration is cost-effective, using less storage space than mirroring, while still providing data protection.
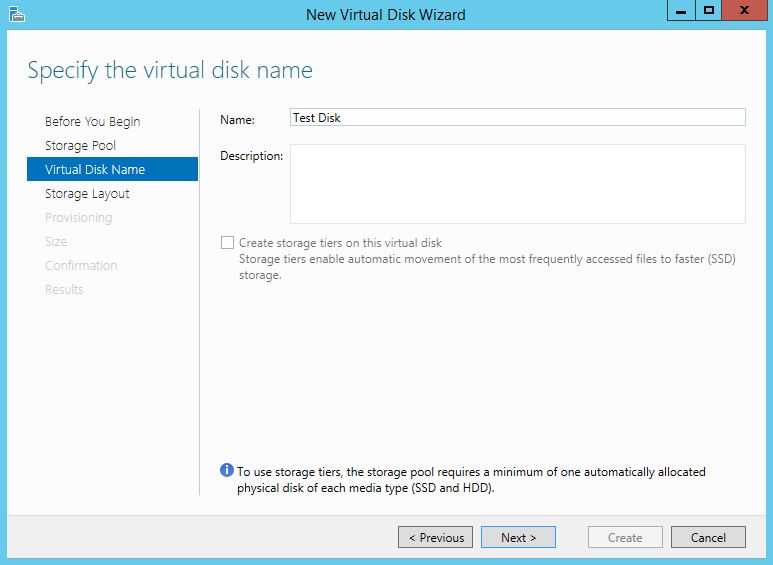
- Tiered Storage: This advanced configuration leverages different types of storage media, such as SSDs and HDDs, to optimize performance and cost. Frequently accessed data is stored on faster media, while less frequently accessed data is stored on slower but more cost-effective media.
Benefits of Storage Spaces
Beyond its flexibility, Storage Spaces in Windows Server offers numerous advantages for organizations:
- Simplified Storage Management: By abstracting physical disks into virtual storage pools, Storage Spaces simplifies storage management. Administrators can easily manage and monitor storage resources, regardless of the underlying hardware configuration.
- Improved Scalability: Storage Spaces allows for the seamless addition of new disks to the storage pool, increasing capacity and performance as needed. This scalability ensures that storage infrastructure can grow alongside organizational needs.
- Enhanced Data Protection: Mirrored and parity storage configurations provide robust data protection against disk failures. This ensures data availability and minimizes downtime, crucial for mission-critical applications.
- Cost Optimization: Utilizing tiered storage and parity configurations, Storage Spaces optimizes storage costs by leveraging different storage media and minimizing storage space requirements. This allows organizations to maximize storage efficiency and reduce overall costs.
- Increased Resilience: By utilizing multiple disks, Storage Spaces enhances storage resilience. In case of a disk failure, the remaining disks ensure data availability and minimize downtime. This is particularly important for mission-critical applications and data.
- Improved Performance: By strategically allocating data across different storage media, tiered storage configurations optimize performance, ensuring fast access to frequently used data.
- Flexibility and Customization: Storage Spaces offers a flexible and customizable platform, allowing administrators to tailor storage configurations to specific workloads and requirements. This empowers organizations to optimize storage resources for their unique needs.
Implementation and Configuration
Implementing and configuring Storage Spaces in Windows Server involves several key steps:
- Hardware Requirements: Ensure that the server meets the minimum hardware requirements for Storage Spaces. This includes sufficient RAM, processor power, and compatible storage devices.
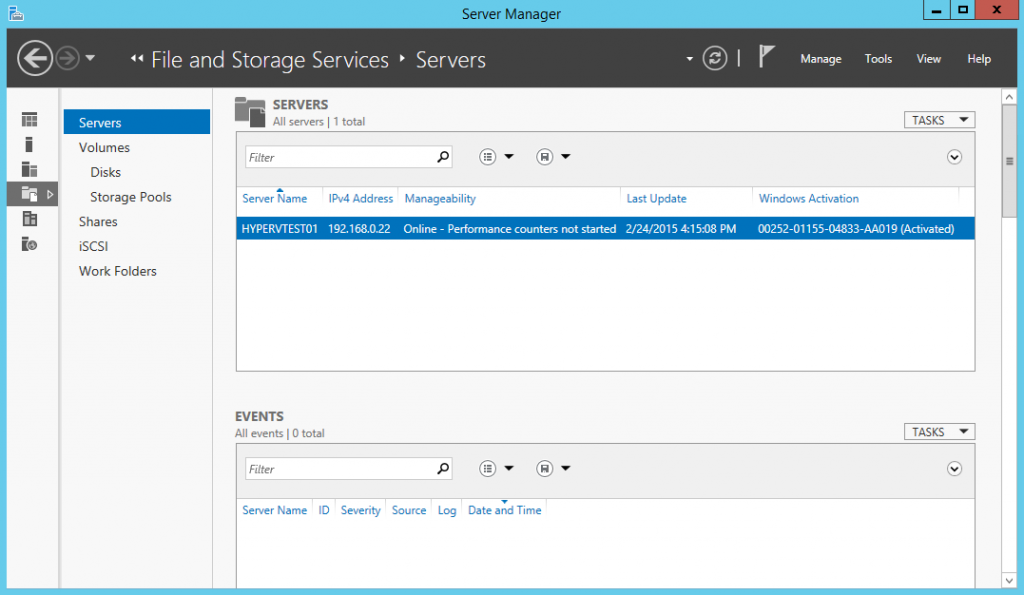
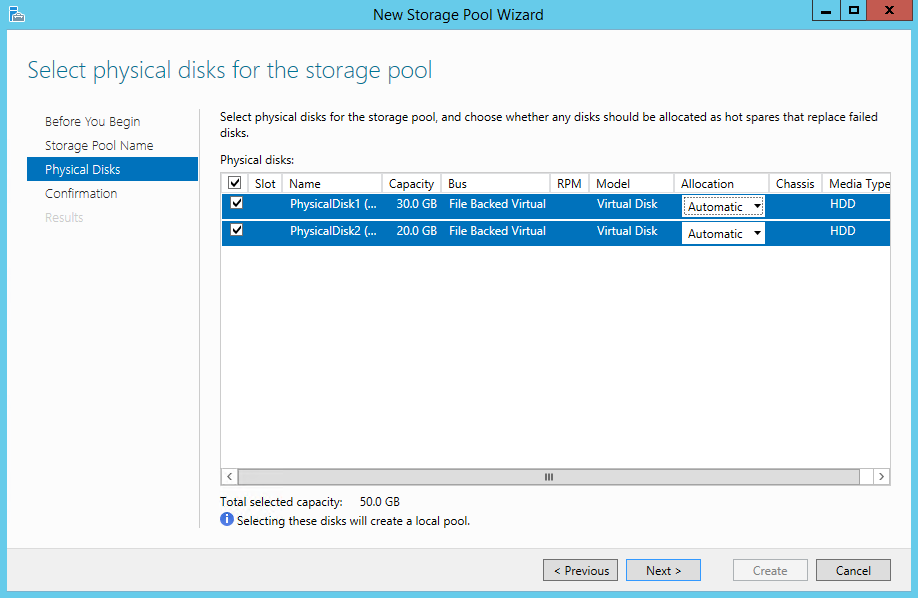
- Storage Pool Creation: Create a storage pool by grouping physical disks together. This step defines the foundation for the virtualized storage space.
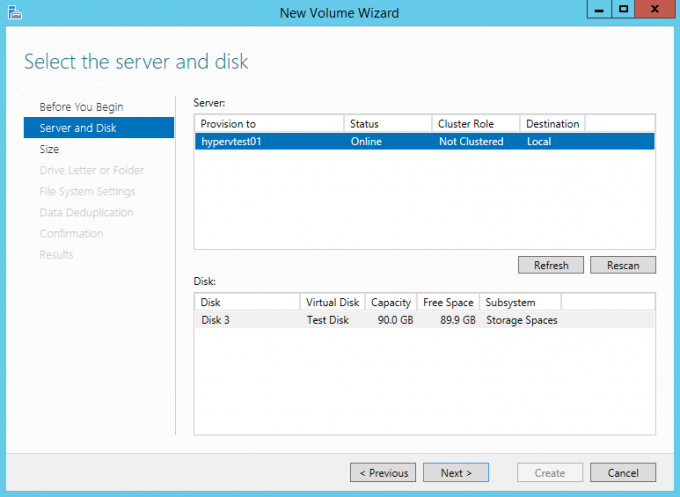
- Volume Creation: Once the storage pool is created, create logical volumes within the pool. These volumes will resemble traditional hard drives and can be formatted and used to store data.
- Storage Configuration: Choose the desired storage configuration, such as simple, mirrored, parity, or tiered storage. This configuration determines how data is stored and protected within the storage pool.
- Resiliency Settings: Configure the resiliency settings for each volume, specifying the number of disks involved in data protection. This ensures data availability and resilience against disk failures.
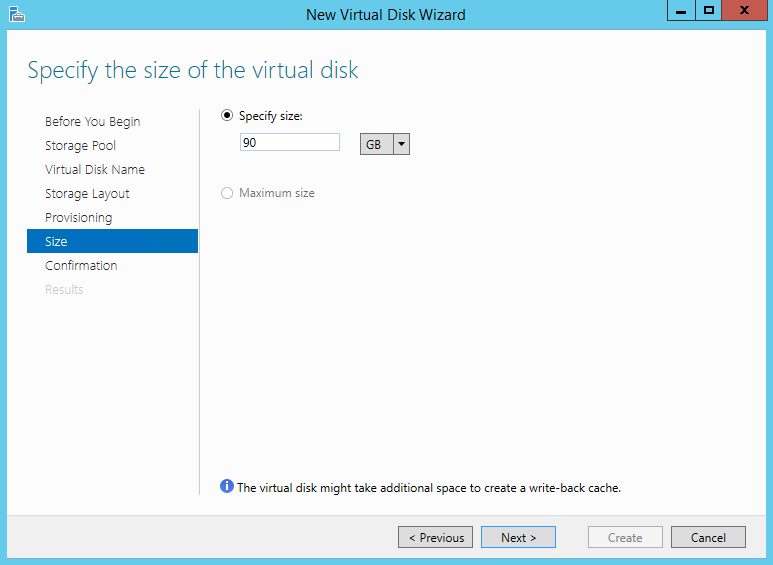
- Capacity Allocation: Allocate storage capacity to each volume based on the anticipated data storage requirements. This ensures that sufficient storage space is available for the intended workloads.
- Volume Formatting and Access: Format the created volumes and assign drive letters for access. This step prepares the volumes for storing data and applications.
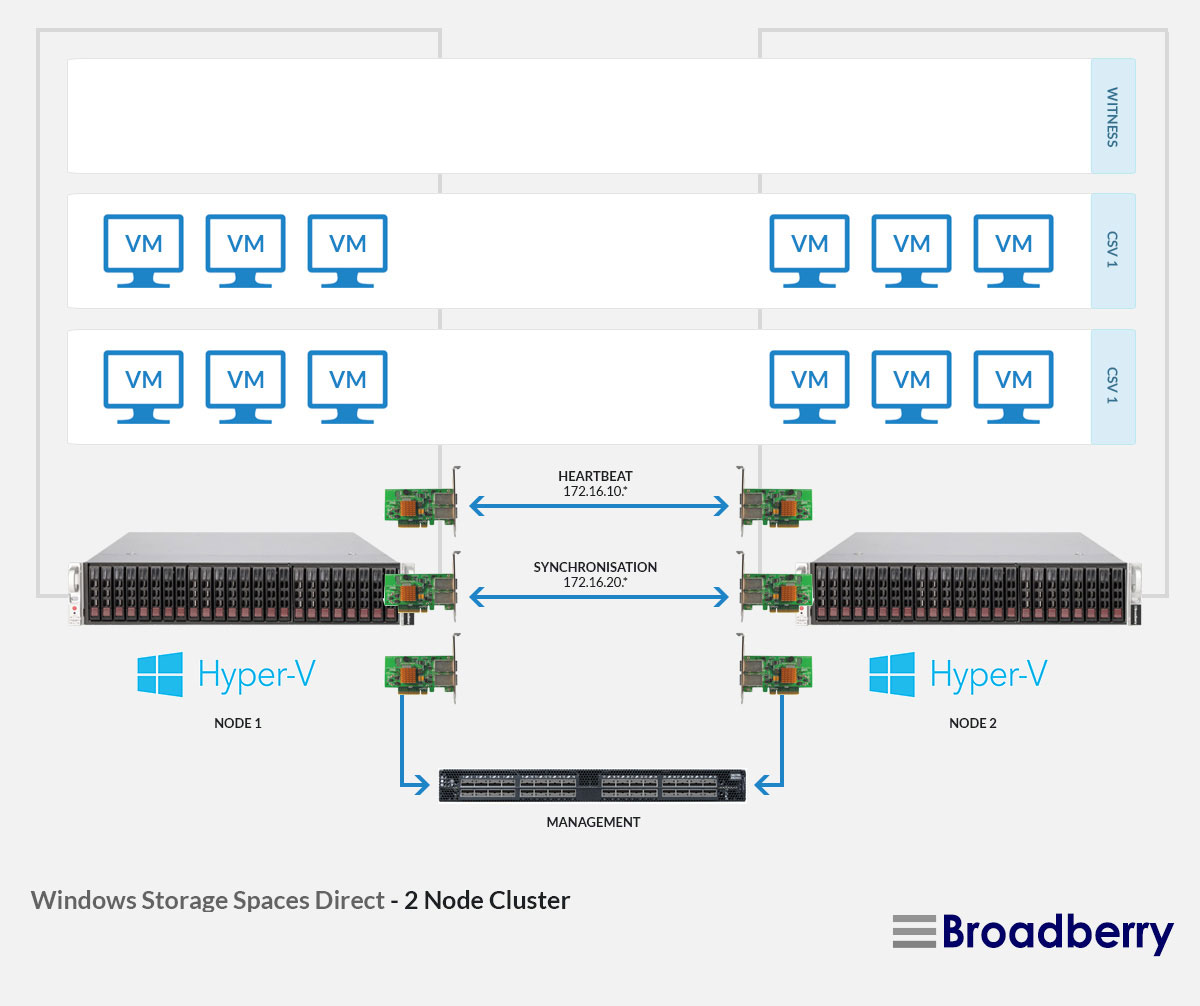
Storage Spaces Direct
For organizations with demanding storage requirements and a need for high availability, Storage Spaces Direct provides an advanced solution. This feature extends the capabilities of Storage Spaces by enabling direct access to physical disks without the need for a separate storage controller. This architecture offers significant benefits, including:
- Reduced Latency: By eliminating the storage controller bottleneck, Storage Spaces Direct significantly reduces latency, enhancing application performance.
- Increased Scalability: Storage Spaces Direct allows for the creation of large-scale storage clusters, enabling the scaling of storage capacity and performance to meet the demands of growing organizations.
- Enhanced Availability: Through the use of multiple servers and redundant storage configurations, Storage Spaces Direct ensures high availability, minimizing downtime and maximizing data accessibility.
Best Practices for Storage Spaces
To maximize the benefits of Storage Spaces in Windows Server, consider these best practices:
- Plan for Growth: Anticipate future storage needs and ensure that the storage pool has sufficient capacity to accommodate growth.
- Choose the Right Configuration: Carefully select the appropriate storage configuration based on the specific workload requirements, balancing performance, cost, and data protection needs.
- Monitor Storage Health: Regularly monitor the health of storage pools, volumes, and disks to identify potential issues proactively.
- Implement Backup and Recovery: Establish a comprehensive backup and recovery plan to protect data from accidental deletion or hardware failures.
- Optimize Performance: Configure storage settings to optimize performance for specific workloads. This includes adjusting disk caching, read/write policies, and other relevant parameters.
- Utilize Automation: Automate routine storage tasks, such as volume creation, disk management, and health monitoring, to improve efficiency and reduce administrative overhead.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the minimum hardware requirements for Storage Spaces in Windows Server?
A: The minimum hardware requirements vary depending on the desired configuration and workload. However, generally, a server needs sufficient RAM, processor power, and compatible storage devices. Refer to the official Microsoft documentation for detailed specifications.
Q: Can I use different types of disks in a storage pool?
A: Yes, you can use different types of disks in a storage pool. However, it’s important to note that performance and cost considerations may apply. For example, using SSDs for frequently accessed data and HDDs for less frequently accessed data can optimize performance and cost.
Q: Can I migrate existing data to Storage Spaces?
A: Yes, you can migrate existing data to Storage Spaces. This can be achieved through various methods, such as using the built-in Windows Server tools or third-party migration software.
Q: What are the advantages of Storage Spaces Direct?
A: Storage Spaces Direct offers significant advantages, including reduced latency, increased scalability, enhanced availability, and simplified management. This solution is ideal for organizations with demanding storage requirements and a need for high availability.
Q: What are the security considerations for Storage Spaces?
A: It’s crucial to implement appropriate security measures for Storage Spaces, including access control, encryption, and regular security audits. This ensures the protection of sensitive data and prevents unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Storage Spaces in Windows Server provides a powerful and flexible storage solution that addresses the evolving storage needs of modern organizations. By enabling the virtualization of storage resources and offering diverse configurations, it simplifies management, enhances data protection, and optimizes costs. With its scalability, resilience, and performance benefits, Storage Spaces empowers organizations to effectively manage their storage infrastructure and ensure reliable data availability. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, Storage Spaces will remain a critical component of their storage strategy, providing a solid foundation for data management and application performance.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Storage Spaces in Windows Server. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
