A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2012 and its End of Support
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2012 and its End of Support
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2012 and its End of Support. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2012 and its End of Support

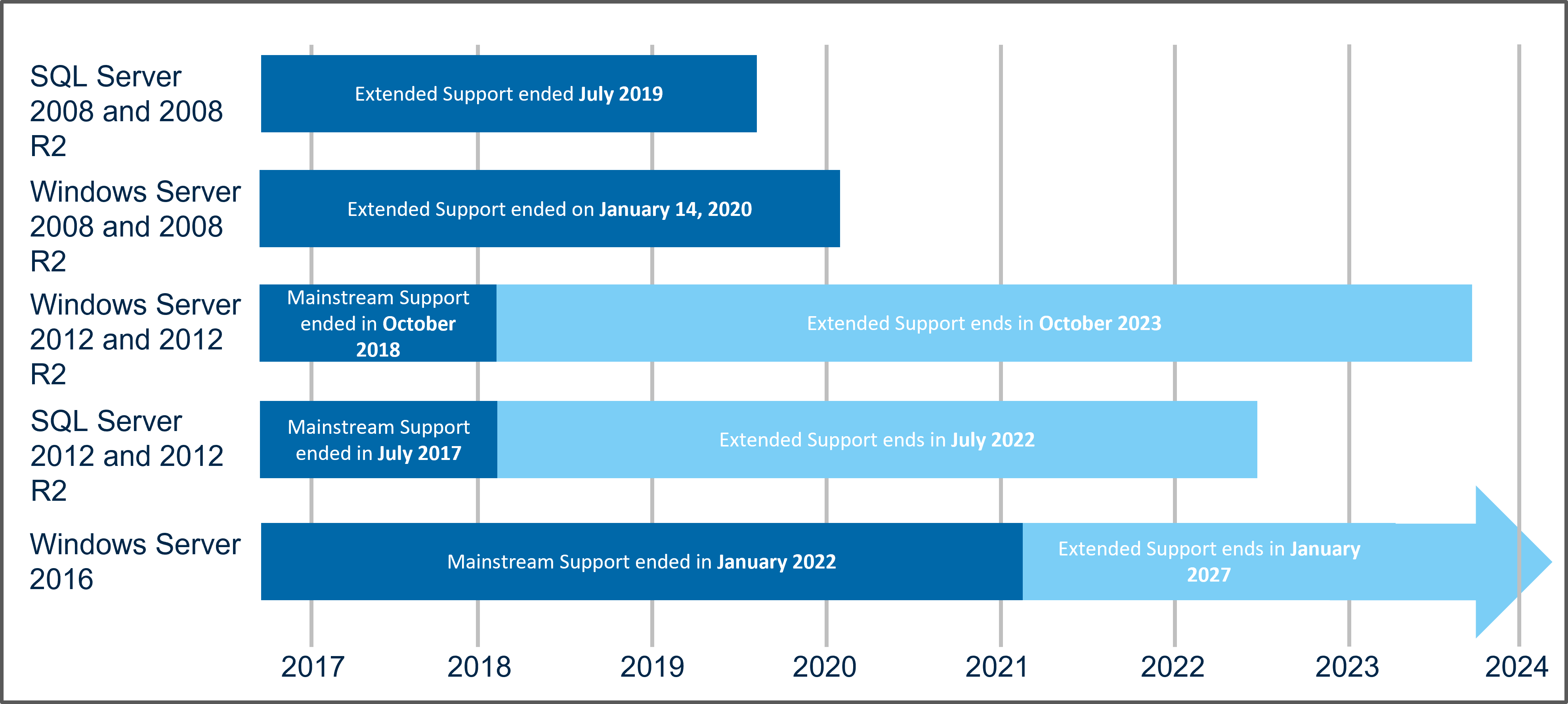
Windows Server 2012, released in 2012, marked a significant step forward in server operating systems, introducing features that revolutionized server management and application deployment. However, as with all technology, the lifecycle of Windows Server 2012 has reached its end, with Microsoft officially ending extended support on October 10, 2023. This signifies the cessation of security updates, bug fixes, and technical support from Microsoft.
Understanding the Importance of Support
While the initial release of Windows Server 2012 brought numerous benefits, the absence of continued support presents several challenges for organizations still relying on this version. These include:
- Security Vulnerabilities: The lack of security patches leaves systems vulnerable to newly discovered exploits, potentially jeopardizing sensitive data and exposing organizations to cyberattacks.
- Compliance Risks: Many industries and regulatory bodies require adherence to specific security standards. Operating unsupported systems can lead to non-compliance, resulting in fines and reputational damage.
- Operational Challenges: Without updates, organizations may experience performance issues, compatibility problems with newer applications, and difficulty troubleshooting technical problems.
- Increased Costs: Organizations may face higher costs associated with managing unsupported systems, including increased security incidents, downtime, and the need for specialized expertise to address technical issues.
Navigating the Transition
The end of support for Windows Server 2012 necessitates a strategic transition plan to mitigate risks and ensure business continuity. This plan should involve the following key considerations:
- Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of all systems running Windows Server 2012, identifying their criticality, dependencies, and potential risks associated with continued use.
- Migration Strategy: Develop a comprehensive migration strategy, considering factors such as the desired target platform, migration timeline, budget, and potential disruptions.
- Technology Choice: Evaluate available options for upgrading or migrating from Windows Server 2012. This may include migrating to a newer version of Windows Server, adopting cloud-based solutions, or exploring alternative operating systems.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorously test the migration process and validate the performance and functionality of systems on the new platform before fully transitioning.
- Training and Documentation: Ensure adequate training for IT staff on the new platform and maintain comprehensive documentation for ongoing management and troubleshooting.
Exploring Alternatives: Windows Server 2019 and Azure
Microsoft offers several compelling alternatives to Windows Server 2012, each with its own advantages and suitability depending on specific organizational needs.
- Windows Server 2019: This latest version of Windows Server delivers enhanced security, performance, and scalability, along with new features like containerization, artificial intelligence (AI), and hybrid cloud capabilities.
- Azure: Microsoft’s cloud platform provides a flexible and scalable solution for hosting applications and services. Azure offers a wide range of services, including virtual machines, storage, databases, and networking, allowing for seamless integration with existing on-premises infrastructure.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What are the key benefits of migrating to Windows Server 2019 or Azure?
A: Migrating to Windows Server 2019 or Azure offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: Newer platforms provide robust security features, including built-in security monitoring, threat detection, and vulnerability mitigation tools.
- Improved Performance: Windows Server 2019 and Azure offer optimized performance, allowing for faster processing, reduced latency, and improved application responsiveness.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based solutions like Azure provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to adjust resources on demand to meet changing business needs.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud solutions can offer cost savings through pay-as-you-go pricing models and reduced infrastructure management overhead.
Q: How can I mitigate the risks associated with running unsupported systems?
A: Mitigating risks associated with unsupported systems requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Implement Strong Security Practices: Adopt robust security practices, including regular security audits, penetration testing, and multi-factor authentication.
- Limit Network Access: Restrict access to vulnerable systems and minimize their exposure to the internet.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate vulnerable systems from critical business networks to prevent lateral movement of attackers.
- Use Security Software: Deploy security software, such as antivirus and intrusion detection systems, to identify and mitigate potential threats.
Q: What are the key considerations for migrating to a new platform?
A: Several key considerations should guide migration decisions:
- Business Requirements: Clearly define business requirements, including performance, security, scalability, and budget constraints.
- Application Compatibility: Ensure that applications are compatible with the new platform, considering potential compatibility issues and necessary upgrades.
- Data Migration: Develop a comprehensive data migration plan, including data backup, transfer, and validation procedures.
- Training and Support: Ensure adequate training for IT staff on the new platform and secure necessary support resources for ongoing management and troubleshooting.
Tips for a Successful Transition
- Start Early: Begin planning the transition well in advance to avoid last-minute rushes and potential disruptions.
- Prioritize Critical Systems: Focus on migrating critical systems first, ensuring minimal business disruption.
- Phased Approach: Implement a phased approach to migration, gradually transitioning systems to the new platform while minimizing risk.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Consult with experienced IT professionals or migration specialists to ensure a smooth and successful transition.
Conclusion
The end of support for Windows Server 2012 presents a critical juncture for organizations still relying on this version. Failing to migrate to a supported platform exposes organizations to significant security risks, compliance issues, and operational challenges. By carefully planning and executing a transition, organizations can mitigate these risks, enhance security posture, and leverage the benefits of newer technologies to drive business innovation and growth.
The transition from Windows Server 2012 provides an opportunity for organizations to embrace modern technologies and improve their overall IT infrastructure. With careful planning and execution, the move to supported platforms can ensure long-term security, stability, and operational efficiency, paving the way for future success.

.jpg#keepProtocol)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2012 and its End of Support. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
