Enabling Virtualization with Hyper-V on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Enabling Virtualization with Hyper-V on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Enabling Virtualization with Hyper-V on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Enabling Virtualization with Hyper-V on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Virtualization, the ability to run multiple operating systems or applications on a single physical machine, has become an indispensable tool for modern IT environments. Microsoft’s Hyper-V, a powerful virtualization platform integrated within Windows Server, offers a robust and efficient solution for organizations of all sizes. This article provides a comprehensive guide to installing and utilizing Hyper-V on Windows Server, exploring its capabilities and benefits in detail.
Understanding Hyper-V and its Role in Modern IT
Hyper-V acts as a hypervisor, a software layer that manages the interaction between the physical hardware and virtual machines (VMs). It creates isolated environments for these VMs, allowing them to run independently, with their own dedicated resources and operating systems. This approach offers numerous advantages:
- Resource Optimization: By consolidating multiple workloads onto a single physical server, organizations can reduce hardware costs, energy consumption, and space requirements.
- Improved Flexibility and Scalability: VMs can be easily created, cloned, and migrated, allowing for rapid deployment of new applications and services, while adapting to changing workload demands.
- Enhanced Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: VMs can be replicated to secondary locations, ensuring business continuity in the event of hardware failures or natural disasters.
- Simplified Management: Hyper-V provides a centralized management interface for creating, configuring, and monitoring VMs, simplifying administrative tasks.
Prerequisites for Installing Hyper-V on Windows Server
Before embarking on the installation process, ensure that your hardware meets the following minimum requirements:
- Processor: Intel VT-x or AMD-V virtualization technology enabled.
- Memory: 2 GB RAM (4 GB recommended).
- Hard Drive: 20 GB free space (40 GB recommended).
- Operating System: Windows Server 2012 or later.
Installing Hyper-V on Windows Server
The installation process for Hyper-V is straightforward and can be completed through the Windows Server Manager interface:
- Open Server Manager: Access the Server Manager by clicking on the "Server Manager" icon in the taskbar or by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Navigate to "Add Roles and Features": In the Server Manager console, click on "Manage" and then "Add Roles and Features."
- Select "Hyper-V": In the "Features" section of the wizard, select "Hyper-V" and click "Next."
- Confirm Installation: Review the prerequisites and click "Install" to initiate the installation process.
Configuring Hyper-V after Installation
Once Hyper-V is installed, you can configure its settings to optimize performance and security:
- Network Configuration: Configure the virtual switch settings to enable communication between VMs and the physical network.
- Storage Configuration: Define the storage locations for VM files and ensure sufficient disk space is available.
- Security Settings: Configure access control policies and other security settings to protect your VMs from unauthorized access.
Creating and Managing Virtual Machines
With Hyper-V installed and configured, you can create and manage VMs to host various applications and services:
- Create a New Virtual Machine: Access the Hyper-V Manager by searching for it in the Start menu. Click "Action" > "New" > "Virtual Machine."
- Configure VM Settings: Specify the name, location, memory, and other settings for the VM.
- Install Operating System: Choose an operating system image and install it on the VM, following the standard installation procedure.
- Manage VMs: Use the Hyper-V Manager to start, stop, pause, and manage the VMs. You can also access the VM console for remote management.
Utilizing Hyper-V for Advanced Virtualization Scenarios
Beyond basic VM creation and management, Hyper-V offers advanced features for complex virtualization scenarios:
- Live Migration: Migrate running VMs between physical servers without downtime, ensuring high availability and business continuity.
- Replication: Create replicas of VMs on other servers, enabling disaster recovery and failover capabilities.
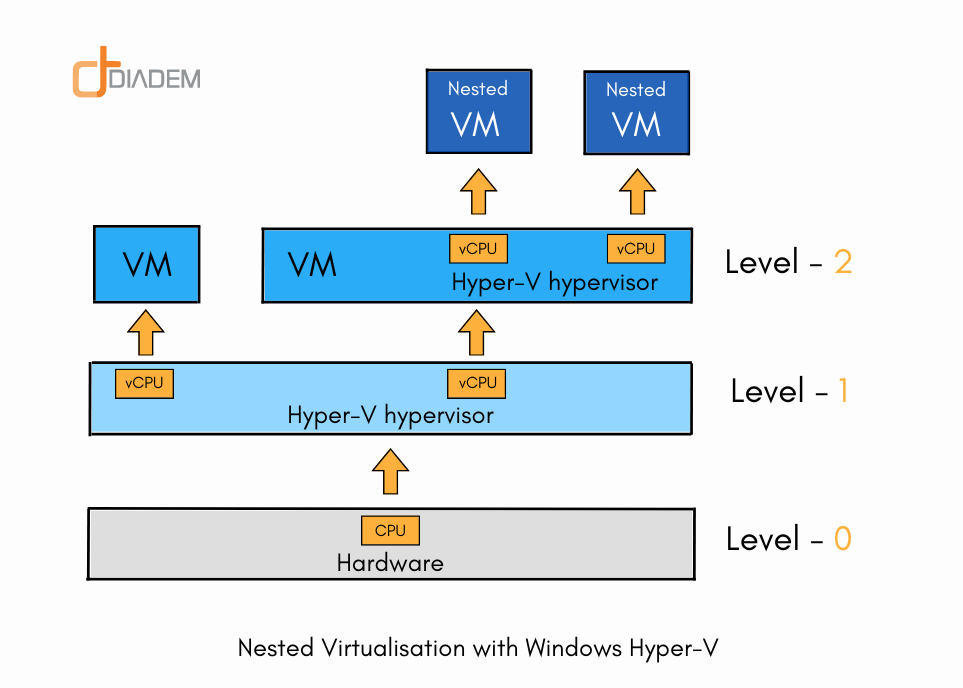
- Nested Virtualization: Run Hyper-V inside a VM, allowing for the creation of nested virtual environments.
- Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) Management: Manage VHD files, including creating, attaching, and detaching them from VMs.
Benefits of Utilizing Hyper-V in Your IT Environment
The implementation of Hyper-V offers numerous benefits, including:
- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware and energy consumption through server consolidation.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined management and simplified deployment of applications and services.
- Enhanced Reliability: Improved fault tolerance and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Improved Security: Isolated environments for VMs enhance security and protect against threats.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Adaptability to changing workload demands and business requirements.
FAQs Regarding Hyper-V on Windows Server
Q: What is the difference between Hyper-V and VMware?
A: Both Hyper-V and VMware are popular virtualization platforms. Hyper-V is a Microsoft product integrated into Windows Server, while VMware is a third-party solution. Both offer similar features and capabilities, but differ in pricing models, compatibility, and management interfaces.
Q: Can I run Windows Server on a Hyper-V VM?
A: Yes, you can run Windows Server on a Hyper-V VM. This is a common practice for creating test environments, deploying applications, and managing multiple server instances.
Q: Is Hyper-V suitable for home users?
A: While Hyper-V is primarily designed for enterprise environments, it can also be used by home users for personal projects or testing purposes. However, it might require more technical expertise compared to consumer-oriented virtualization solutions.
Q: Can I use Hyper-V to run Linux VMs?
A: Yes, Hyper-V supports running Linux VMs alongside Windows VMs. You can install Linux distributions on VMs and manage them using the Hyper-V Manager.
Tips for Optimizing Hyper-V Performance
- Allocate Sufficient Resources: Ensure adequate RAM, CPU, and disk space for VMs to function optimally.
- Configure Virtual Switches: Optimize network settings for efficient communication between VMs and the physical network.
- Use Dynamic Memory: Enable dynamic memory to allocate memory to VMs based on their needs, improving resource utilization.
- Optimize Storage Performance: Choose appropriate storage configurations and optimize disk I/O settings for improved VM performance.
- Monitor and Analyze Performance: Regularly monitor VM performance metrics and identify potential bottlenecks to optimize resource allocation.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Virtualization with Hyper-V
Hyper-V on Windows Server provides a robust and versatile virtualization platform, enabling organizations to optimize resource utilization, enhance flexibility, and improve reliability. By understanding its features and capabilities, organizations can leverage the power of virtualization to streamline IT operations, reduce costs, and achieve their business objectives. As technology continues to evolve, Hyper-V will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of IT infrastructure, empowering organizations to embrace the power of virtualized environments and unlock new possibilities.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Enabling Virtualization with Hyper-V on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
