Maintaining a Secure and Efficient Windows Server Environment: A Guide to Updates
Related Articles: Maintaining a Secure and Efficient Windows Server Environment: A Guide to Updates
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Maintaining a Secure and Efficient Windows Server Environment: A Guide to Updates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Maintaining a Secure and Efficient Windows Server Environment: A Guide to Updates
The ever-evolving landscape of technology necessitates a proactive approach to system maintenance. For organizations relying on Windows Server, staying up-to-date is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, security, and stability. This comprehensive guide outlines the essential steps involved in updating Windows Server, emphasizing the importance of this process for organizations of all sizes.
Understanding the Significance of Updates
Windows Server updates are not merely optional upgrades; they are fundamental to maintaining a secure and efficient IT infrastructure. These updates encompass a broad range of improvements, including:
- Security Patches: Addressing vulnerabilities exploited by malicious actors, protecting against ransomware, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
- Performance Enhancements: Optimizing system resources, improving application responsiveness, and streamlining overall performance.
- Feature Additions: Introducing new functionalities, tools, and capabilities that enhance productivity and efficiency.
- Bug Fixes: Addressing known issues and errors, improving stability and reliability.
The Importance of a Well-Planned Update Strategy
Updating a Windows Server environment is not a task to be undertaken lightly. A well-defined strategy is essential to minimize downtime, prevent data loss, and ensure a smooth transition. The following considerations are crucial:
-
Assessment and Planning:
- Identify the Specific Servers: Determine which servers require updates, their roles within the network, and their criticality to operations.
- Evaluate Compatibility: Verify compatibility of applications, hardware, and other software with the new update.
- Define Scope and Timeline: Establish the extent of the update, including specific features and patches, and set a realistic timeline for implementation.
- Develop a Backup Plan: Ensure reliable backups of all critical data, applications, and configurations before proceeding with the update.
-
Communication and Training:
- Inform Users: Clearly communicate the update schedule and potential impact on users, providing adequate notice and guidance.
- Train Administrators: Equip IT staff with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform the update effectively and troubleshoot any issues.
-
Testing and Validation:
- Perform Thorough Testing: Conduct comprehensive testing in a controlled environment to ensure the update functions as expected and does not cause conflicts with existing systems.
- Validate Functionality: Verify that all critical applications and services are operational after the update.
Methods for Updating Windows Server
There are two primary methods for updating Windows Server:
-
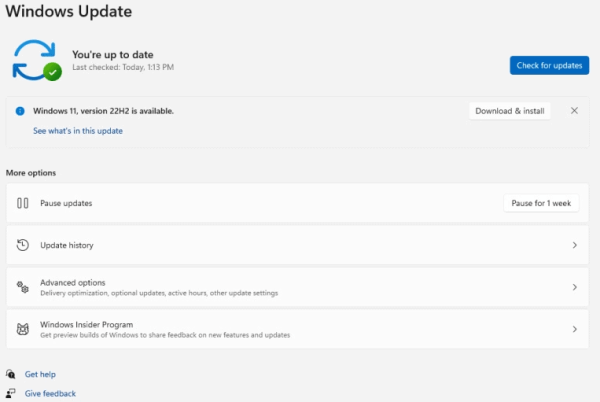
Windows Update: This built-in tool allows for automatic updates, providing a convenient way to stay current. It offers a range of update options, including:
- Automatic Updates: Updates are installed automatically at scheduled times, minimizing manual intervention.
- Manual Updates: Users can select specific updates to install based on their needs and priorities.
- Deferred Updates: Updates can be delayed for a specific duration to allow for planning and testing.
-
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): This centralized server management tool enables administrators to control and manage updates across multiple servers within a network. Benefits include:
- Centralized Management: Streamline update deployment and management across the entire server infrastructure.
- Content Caching: Reduce bandwidth consumption by storing update files locally, making updates more efficient.
- Approval and Deployment: Control which updates are deployed to specific servers and schedule update deployments for optimal timing.
Steps for Updating Windows Server
Once a comprehensive update strategy is in place, follow these steps to update your Windows Server:
-
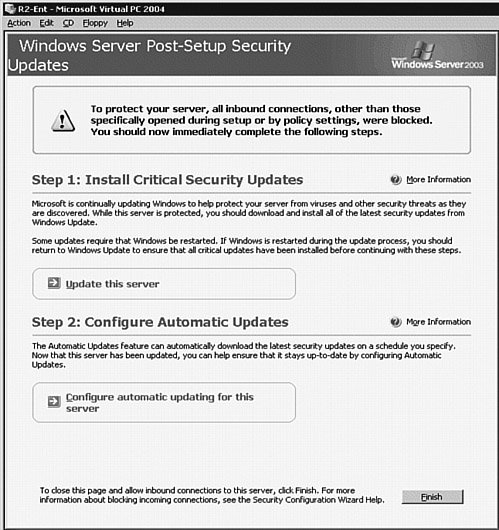
Prepare for the Update:
- Backup Data: Create a full backup of the server to ensure data recovery in case of unexpected issues.
- Check Compatibility: Verify that applications, hardware, and other software are compatible with the new update.
- Review Update History: Check the update history for any known issues or potential conflicts.
-
Install the Update:
- Use Windows Update: Access Windows Update through the Settings app or the Control Panel and follow the prompts to download and install the update.
- Utilize WSUS: Configure WSUS to manage updates for multiple servers, and follow the instructions to deploy the update.
-
Post-Update Verification:
- Restart the Server: After installing the update, restart the server to complete the update process.
- Check for Errors: Monitor the server for any errors or warnings after the restart.
- Test Functionality: Verify that all applications and services are functioning correctly after the update.
Addressing Common Update Issues
While updates are generally straightforward, occasional issues may arise. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Compatibility Conflicts: If applications or hardware are incompatible with the new update, consider contacting the vendor for compatibility updates or alternative solutions.
- Update Errors: If an update fails to install, review the error messages and consult Microsoft documentation for troubleshooting steps.
- System Instability: If the server becomes unstable after the update, revert to the previous version by using the System Restore feature or by restoring from a backup.
FAQs about Updating Windows Server
Q: How often should I update my Windows Server?
A: Microsoft recommends installing updates as soon as they are released to ensure optimal security and performance. However, organizations should establish a regular update schedule based on their specific needs and risk tolerance.
Q: What if I have critical applications that are not compatible with the new update?
A: Contact the application vendor to inquire about compatibility updates or alternative solutions. Consider using a testing environment to evaluate the impact of the update on critical applications before deploying it to production servers.
Q: How can I minimize downtime during the update process?
A: Schedule updates during off-peak hours or during planned maintenance windows. Consider using a phased rollout approach, updating servers in groups to minimize the impact on operations.
Q: What if I experience data loss after updating my server?
A: Restore data from the backup created before the update. If the backup is corrupted, contact a data recovery specialist.
Tips for Effective Windows Server Updates
- Automate Updates: Configure Windows Update to automatically install updates to minimize manual intervention.
- Test Updates in a Sandbox Environment: Before deploying updates to production servers, test them in a controlled environment to identify potential issues.
- Monitor Update Status: Regularly monitor the server for update status and any error messages.
- Keep a Record of Updates: Maintain a log of all updates installed on the server to track changes and troubleshoot issues.
Conclusion
Updating Windows Server is an essential part of maintaining a secure and efficient IT infrastructure. By implementing a well-defined update strategy, organizations can minimize downtime, protect against cyber threats, and ensure optimal performance. Regularly updating servers is not just a technical task; it is a crucial investment in the overall security and reliability of an organization’s technology infrastructure.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Maintaining a Secure and Efficient Windows Server Environment: A Guide to Updates. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
