Managing Windows Updates: A Comprehensive Guide to Server 2022 and Beyond
Related Articles: Managing Windows Updates: A Comprehensive Guide to Server 2022 and Beyond
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Managing Windows Updates: A Comprehensive Guide to Server 2022 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Managing Windows Updates: A Comprehensive Guide to Server 2022 and Beyond

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, ensuring the security and stability of your systems is paramount. Windows Update, Microsoft’s central hub for delivering critical security patches, feature updates, and bug fixes, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy IT environment. However, managing Windows Update effectively, particularly on server systems, requires a nuanced approach. This article delves into the intricacies of Windows Update, specifically focusing on the considerations for Server 2022 and later versions, highlighting best practices and potential scenarios where adjustments might be necessary.
Understanding the Importance of Windows Update
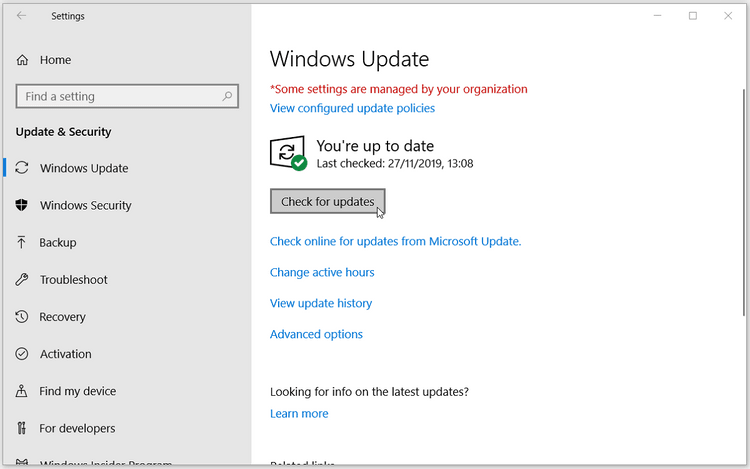
Windows Update serves as a vital lifeline for your systems, continuously delivering updates that enhance security, performance, and functionality. These updates address vulnerabilities, fix bugs, and introduce new features, ensuring that your environment remains protected and up-to-date.
Server 2022 and the Evolution of Windows Update
With the release of Windows Server 2022, Microsoft introduced significant changes to the Windows Update process. These changes aim to streamline the update experience, improve security, and provide greater control to administrators.
Key Considerations for Server 2022 and Later Versions:
-
Semi-Annual Channel (SAC): Server 2022 and subsequent versions are primarily supported through the Semi-Annual Channel (SAC). This channel receives new features and updates twice a year, providing a consistent flow of enhancements.
-
Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC): For specific scenarios where long-term stability and minimal feature updates are prioritized, the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) is available. This channel receives security updates and critical bug fixes for a longer period, typically five years.
-
Flexibility in Update Management: Server 2022 offers administrators greater control over the update process. Features like "Enable Feature Updates" and "Enable Quality Updates" allow for fine-grained control over which updates are applied and when.
-
Automated Updates: Windows Update can be configured for automatic updates, ensuring that systems remain up-to-date without manual intervention. This approach is particularly beneficial for systems that require continuous security and stability.
When to Consider Adjustments to Windows Update
While Windows Update is generally recommended for maintaining a secure and functional environment, there are specific scenarios where adjustments might be necessary:
- Production Environments with Critical Applications: In environments where downtime is unacceptable, applying updates during off-peak hours or implementing a phased rollout strategy is crucial. This minimizes the risk of disruption to critical applications.
- Legacy Systems with Compatibility Issues: Older applications or hardware might have compatibility issues with newer Windows updates. In such cases, careful testing and planning are required to mitigate potential conflicts.
- Specialized Environments: Systems deployed in specialized environments, such as industrial control systems or embedded devices, might have specific security and stability requirements that necessitate customized update management strategies.
Best Practices for Managing Windows Update
-
Regularly Scan for Updates: Set up a schedule for scanning for updates to ensure that your systems are aware of the latest available patches.
-
Prioritize Security Updates: Security updates should be applied as soon as possible to address vulnerabilities and mitigate potential threats.
-
Test Updates in a Test Environment: Before deploying updates to production systems, test them in a controlled environment to identify potential issues and ensure compatibility.
-
Document the Update Process: Maintain clear documentation of the update process, including the steps involved, testing procedures, and rollback strategies.
-
Monitor System Performance: Monitor system performance after applying updates to identify any potential issues or performance degradation.
FAQs
Q: What are the different types of Windows updates?
A: Windows updates fall into two primary categories:
- Security Updates: These updates address vulnerabilities and security flaws, protecting systems from malicious attacks.
- Feature Updates: These updates introduce new features, functionalities, and improvements to the operating system.
Q: How often should I update my server?
A: For Server 2022 and later versions, it is generally recommended to apply updates as soon as they become available, especially security updates. However, in production environments, a phased rollout or applying updates during off-peak hours might be necessary to minimize downtime.
Q: What happens if I don’t update my server?
A: Not updating your server can leave it vulnerable to security threats, expose it to malware, and potentially lead to performance issues. Additionally, systems that are not updated might not be eligible for future support or updates.
Q: How can I disable Windows Update on my server?
A: Disabling Windows Update is generally not recommended. However, in specific scenarios where updates pose a risk to critical applications or infrastructure, temporary disabling might be considered. This should be done with caution and only after careful evaluation and planning.
Tips for Managing Windows Update
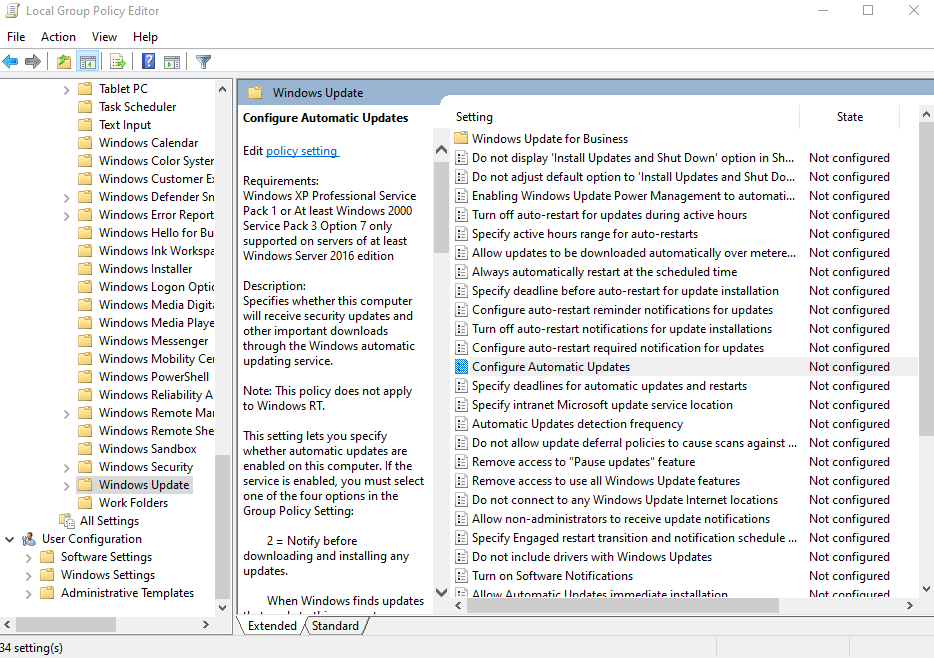
- Utilize Group Policy: Group Policy provides a powerful mechanism for managing Windows Update settings across multiple systems.
- Configure Update Delivery Optimization: Update Delivery Optimization (UDO) allows systems to share update files with each other, reducing download times and network bandwidth usage.
- Implement a Patch Management Solution: Consider using a dedicated patch management solution to automate the update process, track updates, and manage deployments.
- Stay Informed about Updates: Subscribe to Microsoft’s security bulletins and update notifications to stay informed about new releases and important updates.
Conclusion
Managing Windows Update effectively is crucial for maintaining a secure, stable, and functional IT environment. Server 2022 and later versions offer enhanced control and flexibility over the update process, allowing administrators to tailor update strategies to their specific needs. By understanding the importance of updates, following best practices, and addressing potential challenges, organizations can ensure their systems remain protected and perform optimally.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Windows Updates: A Comprehensive Guide to Server 2022 and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
