Navigating the Landscape of Microsoft Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Microsoft Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Microsoft Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Microsoft Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide

The world of software licensing can be complex, particularly when dealing with a multifaceted operating system like Microsoft Windows Server. Understanding the intricacies of licensing is crucial for organizations to ensure compliance, optimize costs, and maximize the value of their technology investments. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of Microsoft Windows Server licensing, focusing on the key considerations for successful deployment and management.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Windows Server Licensing
Microsoft Windows Server licensing is based on a core concept: per-processor licensing. This means that each physical processor within a server requires a separate license. Each processor can support multiple cores, but the licensing is tied to the physical processor itself. This approach ensures that organizations pay for the processing power they utilize.
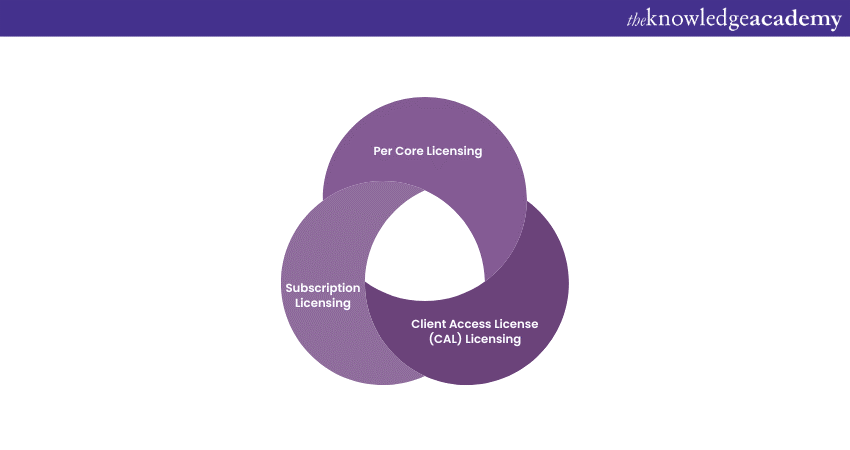
Key Licensing Models for Windows Server
Microsoft offers a variety of licensing models for Windows Server, each catering to specific needs and deployment scenarios. Understanding these models is crucial for making informed decisions:
-
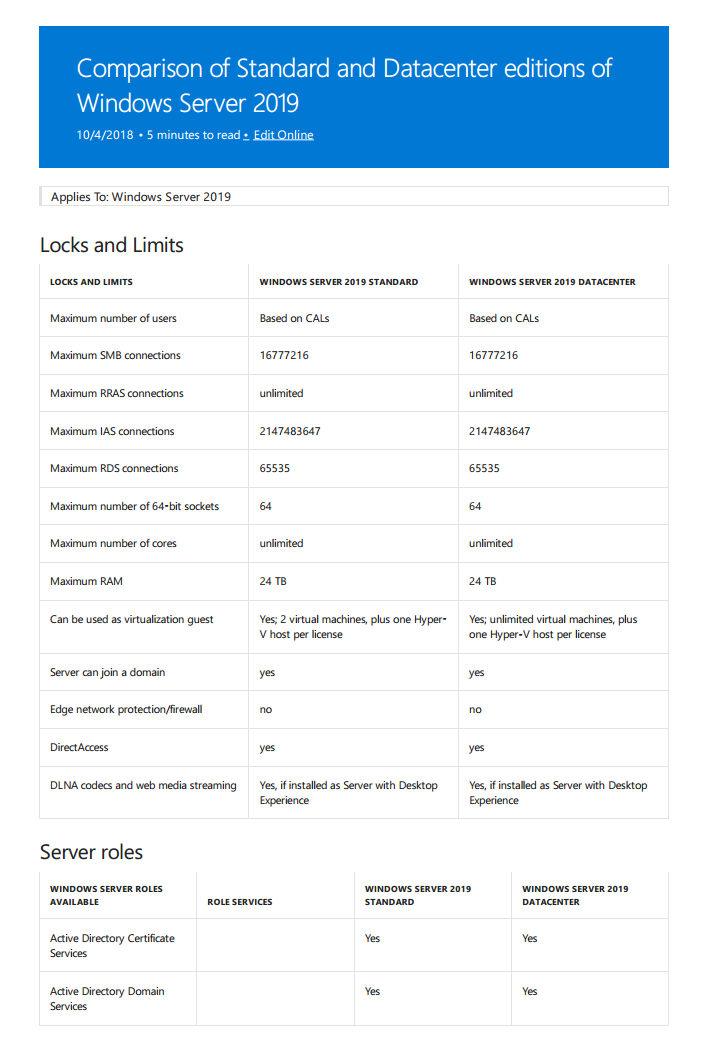
Standard Edition: This edition is designed for small to medium businesses, offering essential server functionalities like file sharing, print services, and basic virtualization. It’s typically suitable for environments with modest workloads and limited server virtualization requirements.
-
Datacenter Edition: This edition is geared towards larger organizations with demanding workloads and extensive virtualization needs. It offers advanced features such as unlimited virtual machines, advanced networking capabilities, and support for high-performance computing.
-
Essentials Edition: This edition is specifically designed for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices. It provides a simplified and cost-effective solution for basic server needs.
-
Azure Edition: This edition is specifically designed for running Windows Server on Azure, offering a streamlined approach for cloud deployments.
Understanding Software Assurance (SA)
Software Assurance (SA) is an optional program offered by Microsoft that provides ongoing benefits alongside Windows Server licensing. SA offers several advantages, including:
-
New Version Rights: SA grants access to the latest versions of Windows Server as they become available, allowing organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest features and security enhancements.
-
Training and Support: SA provides access to training materials and technical support resources, helping organizations maximize their use of Windows Server and address any technical challenges they encounter.
-
Software Downloads: SA allows organizations to download and use software from Microsoft’s online distribution platform, providing flexibility and convenience.
Licensing Considerations for Virtualization
Virtualization is a common practice in modern IT environments, allowing organizations to consolidate workloads and optimize resource utilization. Windows Server licensing for virtualization comes with specific considerations:
-
Virtual Machine Licensing: Each virtual machine running Windows Server requires its own separate license, regardless of whether it’s running on a physical server with a Datacenter Edition license.
-
Hyper-V Server Licensing: Microsoft offers a free Hyper-V Server operating system for managing virtual machines. However, each virtual machine running a guest operating system still requires a separate Windows Server license.
-
Virtualization Rights: Datacenter Edition licenses offer unlimited virtualization rights, allowing organizations to run as many virtual machines as needed without additional licensing costs.
Key Considerations for Windows Server Licensing
When planning for Windows Server deployments, organizations should consider the following:
-
Workload Requirements: Identify the specific applications and services that will run on the servers, as this will influence the edition choice and the required licensing.
-
Virtualization Strategy: Determine the virtualization approach and the number of virtual machines planned for deployment, as this will directly impact the licensing needs.
-
Software Assurance: Evaluate the benefits of Software Assurance and determine if it aligns with the organization’s long-term goals and support requirements.
-
Licensing Compliance: Ensure strict adherence to Microsoft’s licensing terms and conditions to avoid potential legal and financial consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Windows Server Licensing
1. How many Windows Server licenses do I need for my organization?
The number of licenses required depends on the number of physical processors in your servers and the specific edition of Windows Server you choose. For instance, if you have two physical processors, you will need two Windows Server licenses.
2. Can I use a Windows Server license on multiple servers?
No, a Windows Server license is tied to a specific physical processor. You cannot use the same license on multiple servers.
3. What are the benefits of Software Assurance?
Software Assurance provides access to new versions of Windows Server, training materials, technical support, and software downloads. It offers ongoing value and helps organizations stay current with the latest advancements.
4. How do I license Windows Server for virtual machines?
Each virtual machine running Windows Server requires its own separate license. Datacenter Edition licenses offer unlimited virtualization rights, while other editions require a separate license for each virtual machine.
5. What are the penalties for non-compliance with Windows Server licensing?
Non-compliance with Microsoft’s licensing terms can result in significant financial penalties, legal action, and potential disruption to your IT operations.
Tips for Optimizing Windows Server Licensing
-
Conduct a thorough audit: Regularly assess your server infrastructure and licensing usage to identify potential areas for optimization and ensure compliance.
-
Embrace virtualization: Leverage virtualization technologies to consolidate workloads and reduce the overall number of physical servers, potentially lowering licensing costs.
-
Consider Software Assurance: Evaluate the benefits of Software Assurance and determine if it aligns with your long-term goals and support requirements.
-
Seek expert guidance: Consult with Microsoft partners or experienced IT professionals to navigate the complexities of Windows Server licensing and ensure optimal deployment and management.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of Microsoft Windows Server licensing requires a thorough understanding of the licensing models, editions, and considerations. By implementing a robust licensing strategy, organizations can ensure compliance, optimize costs, and maximize the value of their Windows Server investments. By understanding the key concepts outlined in this guide, organizations can make informed decisions, optimize their licensing approach, and ensure a smooth and efficient deployment of Windows Server within their IT infrastructure.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Microsoft Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!

