Navigating the Landscape of Windows Server 2012 Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Windows Server 2012 Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Windows Server 2012 Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Windows Server 2012 Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows Server 2012, despite its age, remains a viable option for many organizations, particularly those seeking a robust and reliable server platform with a proven track record. However, acquiring the necessary licenses for this operating system requires careful consideration and understanding of the various licensing models available. This article provides a comprehensive guide to Windows Server 2012 licensing, demystifying the process and equipping potential users with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding the Licensing Models:
Windows Server 2012 licensing revolves around two primary models:
-
Per-Processor Licensing: This model, commonly used for physical servers, requires a license for each processor core within the server. Each license grants access to the operating system and its features, enabling the server to manage and execute applications, handle network traffic, and provide storage services.
-
Per-Device Licensing: This model, suitable for virtualized environments, grants access to the operating system for a specific virtual machine (VM). Each VM requires a separate license, regardless of the number of physical cores it utilizes. This model allows for greater flexibility and resource optimization, as organizations can allocate resources based on actual needs.
Choosing the Right Licensing Model:
The choice between per-processor and per-device licensing hinges on the specific needs and architecture of the organization’s infrastructure.
-
Physical Server Environments: Organizations with predominantly physical servers will find per-processor licensing more cost-effective, as it aligns directly with the physical hardware configuration.
-
Virtualized Environments: Organizations utilizing virtualization technologies, such as Hyper-V or VMware, will benefit from per-device licensing. This model provides greater flexibility in resource allocation, allowing for efficient utilization of hardware and reduced licensing costs.
Key Licensing Components:
Understanding the different components of Windows Server 2012 licensing is crucial for making informed decisions:
-
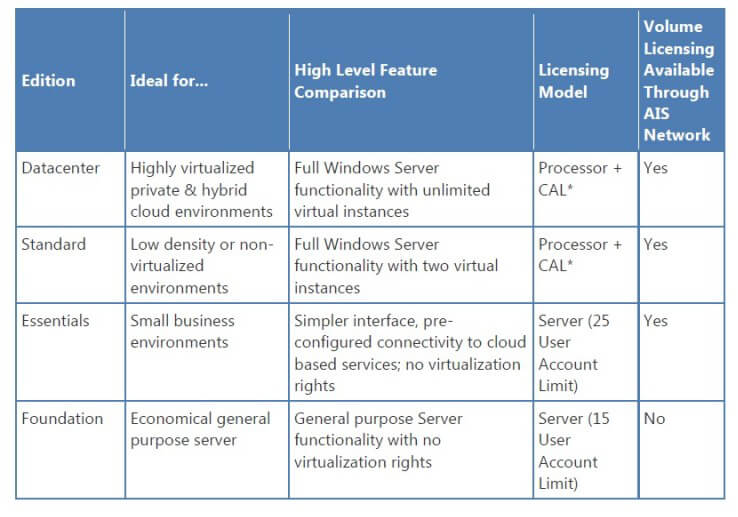
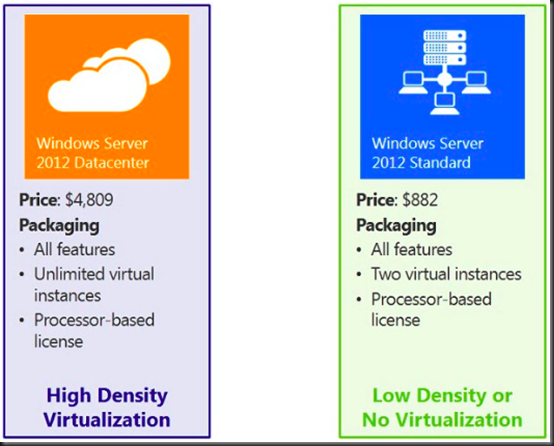
Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition: This edition provides a comprehensive set of features for general-purpose servers, including file and print services, web server capabilities, and remote desktop services. It is suitable for small to medium-sized businesses and organizations with basic server needs.
-
Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition: This edition offers advanced features specifically designed for high-performance computing, virtualization, and mission-critical applications. It caters to large enterprises with demanding infrastructure requirements and complex data management needs.
-
Client Access Licenses (CALs): CALs are required for each user or device accessing a Windows Server 2012 server. These licenses grant permissions to utilize the server’s resources and functionalities, such as accessing shared files, printing documents, or utilizing remote desktop services.
Factors Influencing Licensing Costs:
Several factors influence the overall cost of Windows Server 2012 licensing:
-
Edition: Datacenter Edition typically carries a higher price tag than Standard Edition due to its expanded feature set.
-
Number of Processors/Cores: The number of physical cores in a server directly impacts the cost under the per-processor licensing model.
-
Number of Users/Devices: The number of users or devices requiring access to the server determines the required number of CALs, contributing to the overall licensing expense.
Software Assurance:
Software Assurance (SA) is an optional program that provides additional benefits, including:
-
Upgrade Rights: Access to newer versions of Windows Server as they become available.
-
Training and Support: Access to technical support and training resources.
-
License Mobility: The ability to transfer licenses between servers or environments.
Obtaining Windows Server 2012 Licenses:
Organizations can acquire Windows Server 2012 licenses through authorized Microsoft partners or directly from Microsoft. It is essential to purchase licenses from legitimate sources to ensure authenticity and prevent potential legal issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Can I use Windows Server 2012 on a virtual machine?
A: Yes, Windows Server 2012 can be used on a virtual machine. However, you need to ensure that you have the appropriate per-device licenses for each virtual machine running the operating system.
Q: Do I need a CAL for each user accessing the server?
A: Yes, each user accessing a Windows Server 2012 server requires a User CAL. Additionally, each device accessing the server requires a Device CAL.
Q: What happens if I exceed the number of licenses I have?
A: Operating a server with insufficient licenses is a violation of Microsoft’s licensing agreement and can result in legal consequences, including fines and penalties.
Q: Can I downgrade from Windows Server 2012 to a previous version?
A: Downgrading to a previous version of Windows Server is generally not permitted under Microsoft’s licensing terms.
Q: What are the benefits of Software Assurance?
A: Software Assurance offers several benefits, including upgrade rights, training and support resources, and license mobility.
Tips for Managing Windows Server 2012 Licensing:
-
Conduct a thorough assessment of your infrastructure: Identify the number of servers, processors, and users requiring access to the server to determine the necessary licenses.
-
Consider virtualization: Virtualization can significantly reduce licensing costs by allowing you to consolidate servers and optimize resource utilization.
-
Explore Software Assurance: Evaluate the benefits of Software Assurance to determine if it aligns with your organization’s needs.
-
Partner with a reputable reseller: Engage with a Microsoft partner experienced in Windows Server licensing to ensure compliance and optimize your licensing strategy.
Conclusion:
Acquiring Windows Server 2012 licenses requires careful consideration of the licensing models, editions, and components. By understanding the licensing landscape and making informed decisions, organizations can ensure compliance with Microsoft’s licensing agreements and optimize their server infrastructure for performance, security, and cost-effectiveness. Remember, navigating the complex world of software licensing is crucial for achieving long-term success and avoiding potential legal complications.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Windows Server 2012 Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
