Navigating the Lifespan of Microsoft Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Lifespan of Microsoft Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Lifespan of Microsoft Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Lifespan of Microsoft Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
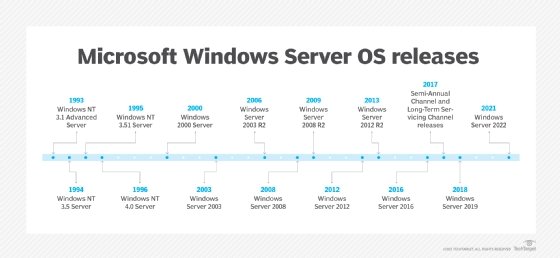
The longevity of any technology is not solely defined by its initial capabilities but also by the support and maintenance it receives throughout its lifespan. Microsoft Windows Server, a cornerstone of many organizations’ IT infrastructure, is no exception. Understanding the lifecycle of a Windows Server release, from its initial launch to its eventual retirement, is crucial for businesses to plan for updates, manage security risks, and ensure long-term operational stability.
Understanding the Lifecycle Stages
Microsoft’s lifecycle policy for Windows Server outlines the stages a release goes through, each with specific support and maintenance commitments. These stages are:
1. Mainstream Support: This phase marks the active development and support period for a Windows Server release. During this time, Microsoft provides:
- Security Updates: Regular security updates address vulnerabilities and protect against potential threats.
- Non-Security Updates: Updates for bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features are released.
- Technical Support: Microsoft offers technical assistance through various channels, including documentation, online forums, and direct support services.
2. Extended Support: After the mainstream support phase ends, a Windows Server release enters extended support. This phase provides a reduced level of support, focusing primarily on:
- Security Updates: Critical security updates are still released to address severe vulnerabilities.
- Technical Support: Limited technical assistance is available for critical issues, but new feature updates are discontinued.
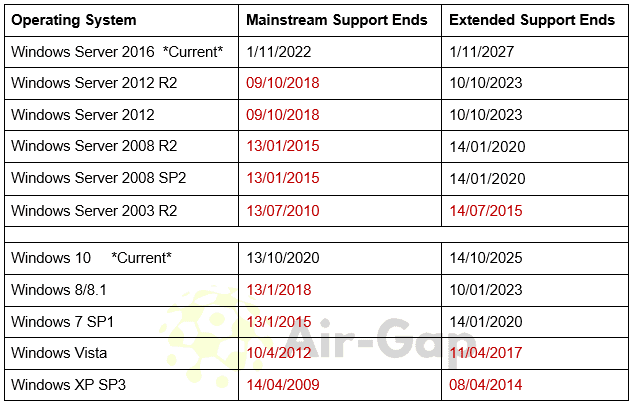
3. End of Support: The final stage marks the end of all support for a Windows Server release. No further security or non-security updates, bug fixes, or technical assistance are provided. This phase emphasizes the crucial need for organizations to migrate to a supported version to ensure security and stability.
Importance of the Lifecycle
Understanding the lifecycle of a Windows Server release is essential for businesses due to its significant impact on:
- Security: Staying within a supported lifecycle ensures access to the latest security updates, mitigating vulnerabilities and protecting sensitive data.
- Stability: Regularly updated servers operate more efficiently and reliably, reducing downtime and minimizing operational disruptions.
- Compliance: Many regulatory bodies mandate the use of supported software, and staying within the lifecycle helps organizations comply with these requirements.
- Planning and Budgeting: The lifecycle provides a framework for businesses to plan future upgrades, allocate resources, and budget for software licensing and maintenance.
Navigating the Lifecycle: A Practical Guide
To navigate the lifecycle effectively, organizations need to adopt a proactive approach:
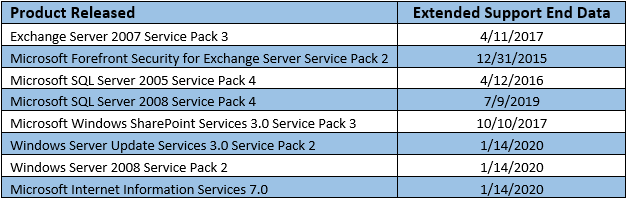
- Monitor Support Dates: Regularly check the Microsoft Lifecycle website for the support end dates of deployed server versions. This allows for timely planning and migration to newer, supported releases.
- Develop a Migration Strategy: Implement a comprehensive plan for migrating to newer versions, considering factors like data migration, application compatibility, and potential infrastructure changes.
- Utilize Microsoft’s Tools and Resources: Leverage tools like the "Windows Server Update Services" (WSUS) for streamlined update management and the "Microsoft Assessment and Planning Toolkit" (MAP) for evaluating migration readiness.
- Engage with Microsoft Support: Contact Microsoft support for expert guidance on migration planning, troubleshooting, and best practices.
FAQs about the Windows Server Lifecycle
Q: How long is the mainstream support phase for Windows Server releases?
A: The mainstream support phase for most Windows Server releases is typically 5 years.
Q: What happens when a server reaches the end of support?
A: Once a server reaches the end of support, it becomes vulnerable to security threats, and Microsoft no longer provides updates or technical support.
Q: Is it always necessary to migrate to a newer version when a server reaches end of support?
A: While migration is highly recommended for security and stability, organizations can sometimes opt for a "supported extended security update" (ESU) for a limited period if they have compelling reasons.
Q: How can I find out the support end date for my current Windows Server version?
A: You can find this information on the Microsoft Lifecycle website or by using the "System Information" tool in Windows.
Tips for Effective Lifecycle Management
- Proactive Planning: Develop a comprehensive lifecycle management plan that includes monitoring support dates, scheduling upgrades, and allocating resources.
- Regular Updates: Implement a process for regular updates, including both security and non-security updates, to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Thorough Testing: Before deploying any major updates or migrations, conduct thorough testing in a controlled environment to minimize potential disruptions.
- Documentation and Training: Maintain detailed documentation of the server environment and provide adequate training to IT staff on lifecycle management practices.
Conclusion
The Microsoft Windows Server lifecycle is a fundamental aspect of managing IT infrastructure effectively. By understanding the lifecycle stages, support policies, and best practices, organizations can ensure their servers remain secure, stable, and compliant. Proactive planning, regular updates, and a commitment to ongoing maintenance are crucial for maximizing the value of Windows Server and minimizing potential risks. Staying informed about the lifecycle and implementing effective strategies will ultimately contribute to a robust and reliable IT environment.


![Windows Server 2008 End of Life upgrade strategies [GUIDE]](https://www.sourceonetechnology.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Supported-in-place-upgrades-for-various-Windows-Server-operating-systems-Image-courtesy-of-Microsoft-1184x623.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Lifespan of Microsoft Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!