Navigating the Path to Modernized IT: A Guide to Windows Server Upgrades
Related Articles: Navigating the Path to Modernized IT: A Guide to Windows Server Upgrades
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Path to Modernized IT: A Guide to Windows Server Upgrades. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Path to Modernized IT: A Guide to Windows Server Upgrades

The digital landscape is in constant flux, demanding businesses to adapt and evolve their IT infrastructure to keep pace. This evolution often necessitates upgrading operating systems, a critical step in ensuring security, performance, and compatibility with emerging technologies. For organizations relying on Windows Server, the decision to upgrade is not merely an option, but a strategic imperative.
While Microsoft has not yet released a Windows Server 2025, the discussion surrounding future versions of the operating system highlights the importance of proactive planning for future upgrades. This guide explores the considerations, processes, and best practices for navigating the path to a modernized IT environment, ensuring a seamless transition and maximizing the benefits of a robust, secure, and future-proof platform.
Understanding the Importance of Upgrading
The decision to upgrade Windows Server is not driven by mere technological curiosity. It is a strategic move that yields tangible benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: Newer server versions incorporate advanced security features, strengthening defenses against evolving cyber threats. This includes robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and enhanced security protocols, mitigating risks and safeguarding sensitive data.
- Improved Performance and Efficiency: Modern server releases are optimized for speed and resource utilization, boosting application performance and reducing operational costs. These advancements translate into faster processing, improved scalability, and a more responsive user experience.
- Increased Compatibility and Innovation: Upgrading ensures compatibility with emerging technologies, enabling the integration of cutting-edge solutions and unlocking new opportunities for business growth. This includes seamless integration with cloud platforms, AI tools, and other modern applications, paving the way for innovation and competitive advantage.
- Extended Support and Maintenance: Staying current with the latest server releases provides access to extended support and maintenance, ensuring ongoing technical assistance and critical security updates. This proactive approach mitigates risks associated with unsupported software, preventing vulnerabilities and potential downtime.
Preparing for the Upgrade: A Step-by-Step Approach
The process of upgrading to a newer version of Windows Server requires careful planning and execution. This comprehensive approach ensures a smooth transition, minimizes disruption, and maximizes the benefits of the upgrade:
1. Assessment and Planning:
- Identify Current Environment: Conduct a thorough assessment of your current server environment, including hardware specifications, software applications, network infrastructure, and user profiles. This detailed inventory provides a clear understanding of the existing infrastructure and potential compatibility issues.
- Define Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the objectives of the upgrade, including desired improvements in security, performance, or compatibility. Determine the scope of the upgrade, identifying specific servers, applications, and user groups to be migrated.
- Establish a Timeline and Budget: Develop a realistic timeline for the upgrade process, considering factors such as resource availability, training requirements, and potential downtime. Allocate a budget to cover hardware, software, and professional services, ensuring financial feasibility.
2. Compatibility and Application Testing:
- Software Compatibility: Verify the compatibility of existing applications with the target server version. This includes testing for potential conflicts, ensuring seamless functionality and avoiding disruptions.
- Hardware Requirements: Assess whether your existing hardware meets the minimum system requirements for the new server version. Consider upgrading hardware components or purchasing new servers to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- Pilot Deployment: Implement a pilot deployment of the new server version in a controlled environment to test compatibility, identify potential issues, and refine the upgrade process before rolling it out to production systems.
3. Data Backup and Recovery:
- Comprehensive Backup: Create a complete backup of all data and configurations on the existing server. This backup serves as a safety net, allowing for data recovery in case of unforeseen issues during the upgrade process.
- Test Data Recovery: Perform a test data recovery from the backup to ensure data integrity and the ability to restore critical information in case of an emergency.
- Data Migration Plan: Develop a detailed data migration plan, outlining the procedures for transferring data from the old server to the new server, ensuring data consistency and minimizing downtime.
4. User Training and Communication:
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to users on the new server version, including its features, functionalities, and potential changes in user workflows. This ensures a smooth transition and minimizes user frustration.
- Clear Communication: Communicate the upgrade process clearly and transparently to all stakeholders, including users, management, and IT staff. This includes outlining the schedule, potential downtime, and any changes in user experience.
- Documentation and Support: Provide clear documentation and support resources to users, including FAQs, user manuals, and troubleshooting guides. This empowers users to navigate the new server environment effectively and resolve any issues independently.
5. Implementation and Rollout:
- Installation and Configuration: Install the new server version on the designated hardware, ensuring proper configuration and network connectivity. This includes setting up user accounts, installing applications, and configuring security settings.
- Phased Rollout: Implement a phased rollout of the new server version, starting with a pilot group and gradually expanding to the entire organization. This allows for monitoring, testing, and addressing any issues before a full-scale deployment.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the performance and stability of the new server environment, identifying potential bottlenecks and optimizing configurations to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
6. Post-Upgrade Maintenance:
- Regular Updates: Implement a regular update schedule for the new server version, ensuring timely installation of security patches, bug fixes, and performance enhancements.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor server performance metrics regularly, identifying potential issues and taking corrective actions to maintain optimal functionality and responsiveness.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of security measures and identify potential vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps maintain a secure and resilient IT environment.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. Will I lose my data during the upgrade process?
No, a properly executed upgrade process should not result in data loss. It is crucial to create a complete data backup before the upgrade and test data recovery to ensure data integrity.
2. How much downtime should I expect during the upgrade?
The amount of downtime depends on the scale and complexity of the upgrade. Implementing a phased rollout and carefully planning the migration process can minimize downtime and ensure minimal disruption to business operations.
3. What are the potential costs associated with upgrading?
Upgrade costs can include hardware upgrades, software licenses, professional services, and training. A comprehensive cost analysis should be conducted during the planning phase to ensure financial feasibility.
4. What if my existing applications are not compatible with the new server version?
Compatibility issues can arise, and it is crucial to test applications before the upgrade. If compatibility issues exist, consider alternative solutions such as application upgrades, replacements, or virtualization.
5. How can I ensure the security of my data during the upgrade?
Data security is paramount during the upgrade process. Implement strong security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access control lists, to protect sensitive information.
Tips for a Successful Upgrade:
- Start Early: Begin planning and preparation for the upgrade well in advance of the actual implementation date. This allows for thorough testing, addressing potential issues, and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Engage Expertise: Consider engaging experienced IT professionals or consultants to assist with the upgrade process. Their expertise can streamline the process, minimize risks, and ensure successful implementation.
- Document Every Step: Maintain detailed documentation throughout the upgrade process, recording configurations, troubleshooting steps, and any changes made. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Prioritize User Experience: Focus on minimizing disruptions to users and ensuring a seamless transition to the new server environment. Clear communication, training, and support resources are essential.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on the latest server releases, security updates, and best practices. This ongoing learning ensures that your IT environment remains secure, efficient, and future-proof.
Conclusion
Upgrading to a newer version of Windows Server is a strategic investment in the future of your IT infrastructure. It unlocks significant benefits in terms of security, performance, compatibility, and innovation, empowering your organization to navigate the evolving digital landscape with confidence. By following a structured approach, prioritizing thorough planning, and leveraging available resources, you can ensure a smooth and successful upgrade, reaping the rewards of a modernized and future-proof IT environment.

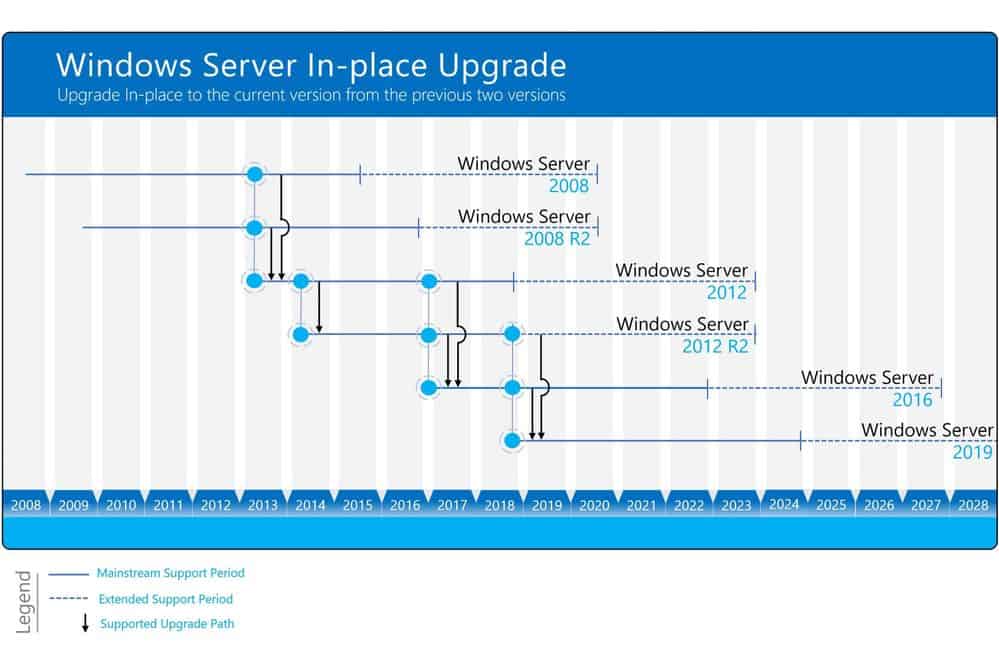
![Windows Server 2008 End of Life upgrade strategies [GUIDE] - EU-Vietnam](https://www.sourceonetechnology.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Windows-Server-2008R2-upgrade-paths-Image-courtesy-of-Microsoft.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Path to Modernized IT: A Guide to Windows Server Upgrades. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
