Navigating the World of Server Virtualization: A Guide to Windows Server and VMware
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Server Virtualization: A Guide to Windows Server and VMware
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Server Virtualization: A Guide to Windows Server and VMware. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Server Virtualization: A Guide to Windows Server and VMware
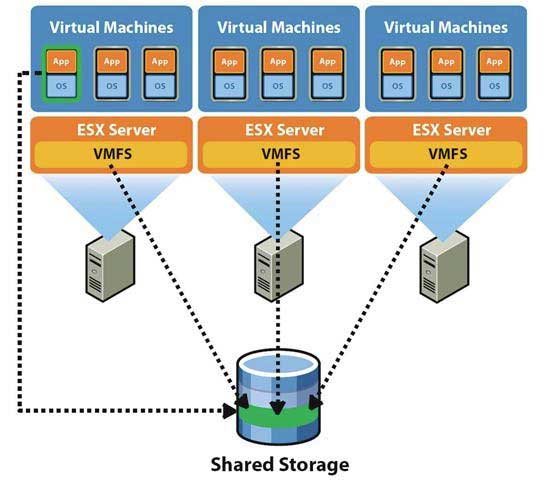
The world of server virtualization is constantly evolving, with new technologies and solutions emerging regularly. At the heart of this dynamic landscape lies the powerful combination of Windows Server and VMware. This pairing empowers organizations to optimize their IT infrastructure, enhance performance, and unlock new levels of flexibility and efficiency. This article delves into the intricacies of this powerful alliance, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding and leveraging the benefits of running Windows Server within a VMware environment.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Windows Server and VMware
Before diving into the specifics of running Windows Server on VMware, it is crucial to grasp the core concepts behind each technology.
Windows Server: This robust operating system is designed specifically for server environments, offering a wide range of features and functionalities critical for businesses of all sizes. It provides a foundation for hosting applications, managing data, and enabling secure network connectivity. Windows Server editions cater to diverse needs, ranging from small businesses to large enterprises, with each edition offering a specific set of features and capabilities.
VMware: This industry-leading virtualization platform revolutionized the way organizations manage their IT infrastructure. VMware allows users to create and run virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. Each VM operates independently, mimicking a physical server and its associated hardware, all within a virtualized environment. This approach offers significant advantages in terms of resource utilization, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
The Synergy of Windows Server and VMware
The integration of Windows Server and VMware represents a powerful synergy that unlocks a range of benefits for organizations:
1. Enhanced Resource Utilization: VMware’s virtualization capabilities enable organizations to consolidate their physical infrastructure, running multiple Windows Server instances on a single physical server. This significantly reduces hardware costs, power consumption, and space requirements, optimizing resource utilization.
2. Increased Flexibility and Agility: Virtualization provides unparalleled flexibility, allowing organizations to quickly deploy and configure new servers or applications without the need for physical hardware provisioning. This agility empowers businesses to respond rapidly to changing demands and adapt to evolving business needs.
3. Improved Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: VMware’s features, such as snapshots and live migration, facilitate seamless disaster recovery and business continuity. In case of hardware failure or other unforeseen events, virtual machines can be quickly restored or migrated to alternative physical servers, minimizing downtime and ensuring business operations continue uninterrupted.
4. Simplified Management and Administration: VMware provides a centralized platform for managing virtual machines and their associated resources. This unified management interface simplifies administration tasks, reduces complexity, and streamlines IT operations.
5. Enhanced Security: VMware offers robust security features, such as virtual machine isolation and network segmentation, to protect virtualized environments from threats. These features help mitigate security risks and safeguard sensitive data stored on virtual machines.
The Journey of Virtualization: Understanding the Process
The process of running Windows Server on VMware involves several key steps:
1. Obtaining the Windows Server ISO Image: The first step is to acquire the appropriate Windows Server ISO image. This image contains the installation files necessary for setting up a Windows Server instance within a VMware environment.
2. Creating a Virtual Machine in VMware: VMware provides a user-friendly interface for creating virtual machines. Users specify the desired configuration, including the amount of RAM, CPU cores, and storage space, to create a virtual environment that meets the specific requirements of the Windows Server instance.
3. Installing Windows Server on the Virtual Machine: Once the virtual machine is created, the Windows Server ISO image is mounted, and the installation process begins. This involves following the standard Windows Server installation steps, including selecting the desired edition, configuring the network settings, and defining the administrator account.
4. Post-Installation Configuration: After the installation is complete, additional configuration steps are required to optimize the Windows Server instance within the VMware environment. This may involve installing necessary drivers, configuring network settings, and setting up applications or services specific to the server’s role.
5. Testing and Validation: Once the Windows Server instance is configured, it is essential to thoroughly test and validate its functionality. This ensures that the server is operating as expected and meets the performance requirements of the intended applications or workloads.
Navigating the Path: A Practical Guide to Windows Server and VMware
Choosing the Right Windows Server Edition: Selecting the appropriate Windows Server edition is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and functionality. Factors to consider include the size of the organization, the intended workload, and the required features.
Understanding VMware’s Virtual Machine Configuration Options: VMware provides a wide range of options for configuring virtual machines, allowing users to tailor the environment to the specific needs of the Windows Server instance. These options include:
- CPU and Memory Allocation: Defining the number of CPU cores and the amount of RAM allocated to the virtual machine.
- Storage Configuration: Selecting the type of storage (e.g., hard disk, SSD) and configuring the storage capacity.
- Network Configuration: Establishing network connectivity for the virtual machine and specifying the network settings.
- Advanced Options: Utilizing advanced features such as snapshots, live migration, and high availability for enhanced flexibility and disaster recovery.
Optimizing Performance and Resources: To maximize the performance of Windows Server within a VMware environment, it is essential to optimize resource allocation and configuration. This involves:
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring sufficient CPU and memory are allocated to the virtual machine to meet the demands of the intended workload.
- Storage Optimization: Selecting the appropriate storage type and configuration to minimize latency and maximize data transfer speeds.
- Network Performance Tuning: Optimizing network settings and configurations to ensure smooth data flow and minimize network bottlenecks.
Addressing Common Challenges: Running Windows Server on VMware may present certain challenges. These challenges can be addressed by:
- Driver Compatibility: Ensuring that all necessary drivers are installed and compatible with the virtualized environment.
- Resource Contention: Monitoring resource usage and adjusting resource allocation as needed to prevent contention between virtual machines.
- Performance Tuning: Regularly reviewing and optimizing performance settings to ensure smooth operation and efficient resource utilization.
FAQs: Demystifying the World of Windows Server and VMware
Q: What are the advantages of running Windows Server on VMware?
A: Running Windows Server on VMware offers numerous advantages, including enhanced resource utilization, increased flexibility and agility, improved disaster recovery and business continuity, simplified management and administration, and enhanced security.
Q: What are the different Windows Server editions available for VMware?
A: Windows Server offers various editions tailored to different needs, including Windows Server Standard, Windows Server Datacenter, and Windows Server Essentials. The choice of edition depends on factors like the size of the organization, the intended workload, and the required features.
Q: How can I ensure the compatibility of Windows Server with VMware?
A: VMware provides extensive documentation and compatibility guides for Windows Server. Refer to these resources to ensure that the chosen Windows Server edition and version are compatible with the VMware environment.
Q: What are some best practices for optimizing the performance of Windows Server on VMware?
A: Best practices include allocating sufficient resources to the virtual machine, selecting appropriate storage configurations, optimizing network settings, and regularly monitoring and adjusting performance settings.
Q: How can I address potential challenges when running Windows Server on VMware?
A: Challenges such as driver compatibility, resource contention, and performance issues can be addressed by installing compatible drivers, monitoring resource usage, and regularly optimizing performance settings.
Tips for Success: Navigating the Path to Efficient Virtualization
- Plan Ahead: Before deploying Windows Server on VMware, carefully plan the virtual machine configuration, resource allocation, and network settings to ensure optimal performance and functionality.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update both Windows Server and VMware to benefit from the latest features, security patches, and performance enhancements.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor resource utilization, performance metrics, and system logs to identify potential issues and optimize the virtualized environment.
- Seek Support: If encountering difficulties or needing guidance, leverage the extensive documentation, online communities, and support resources provided by both Microsoft and VMware.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Server Virtualization
The combination of Windows Server and VMware offers a powerful solution for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure, enhance performance, and unlock new levels of flexibility and efficiency. By understanding the core concepts, navigating the key steps, and implementing best practices, organizations can leverage the full potential of this dynamic duo, embracing the future of server virtualization and driving innovation within their IT landscape.
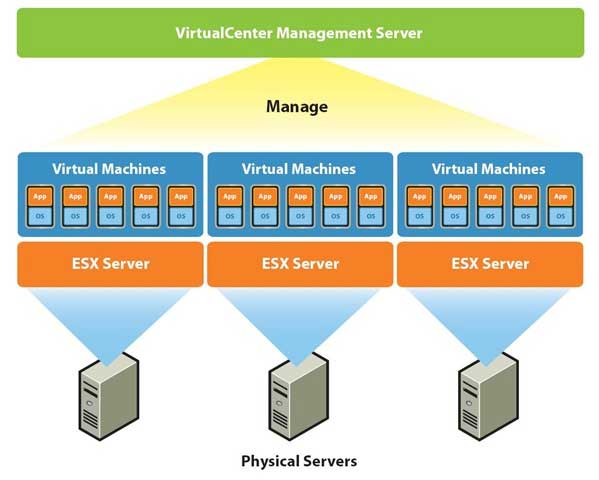



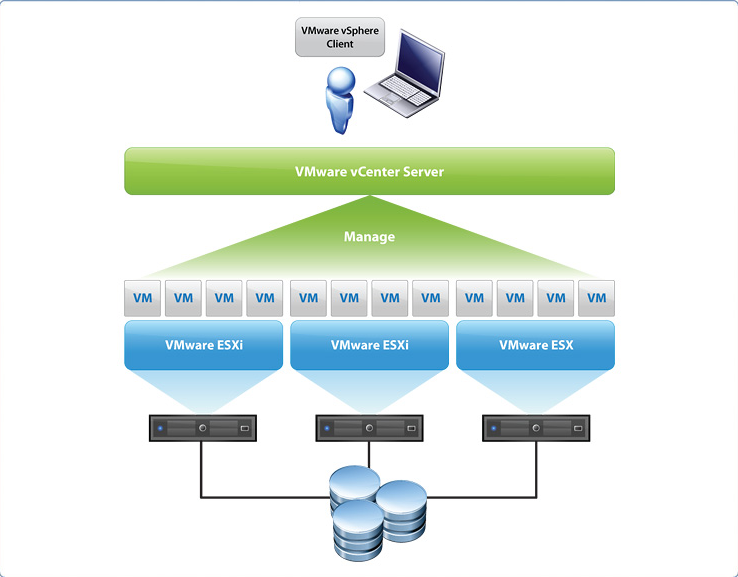
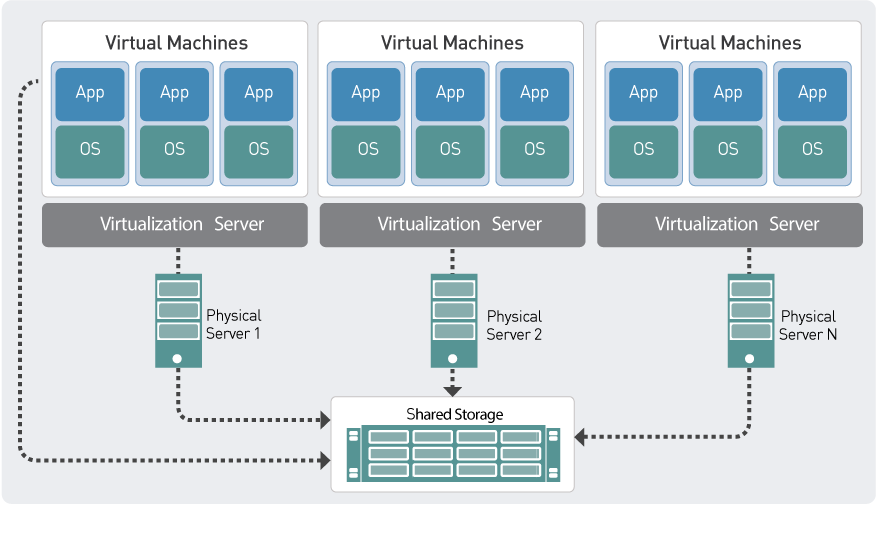

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Server Virtualization: A Guide to Windows Server and VMware. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
