Removing Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Removing Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Removing Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Removing Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
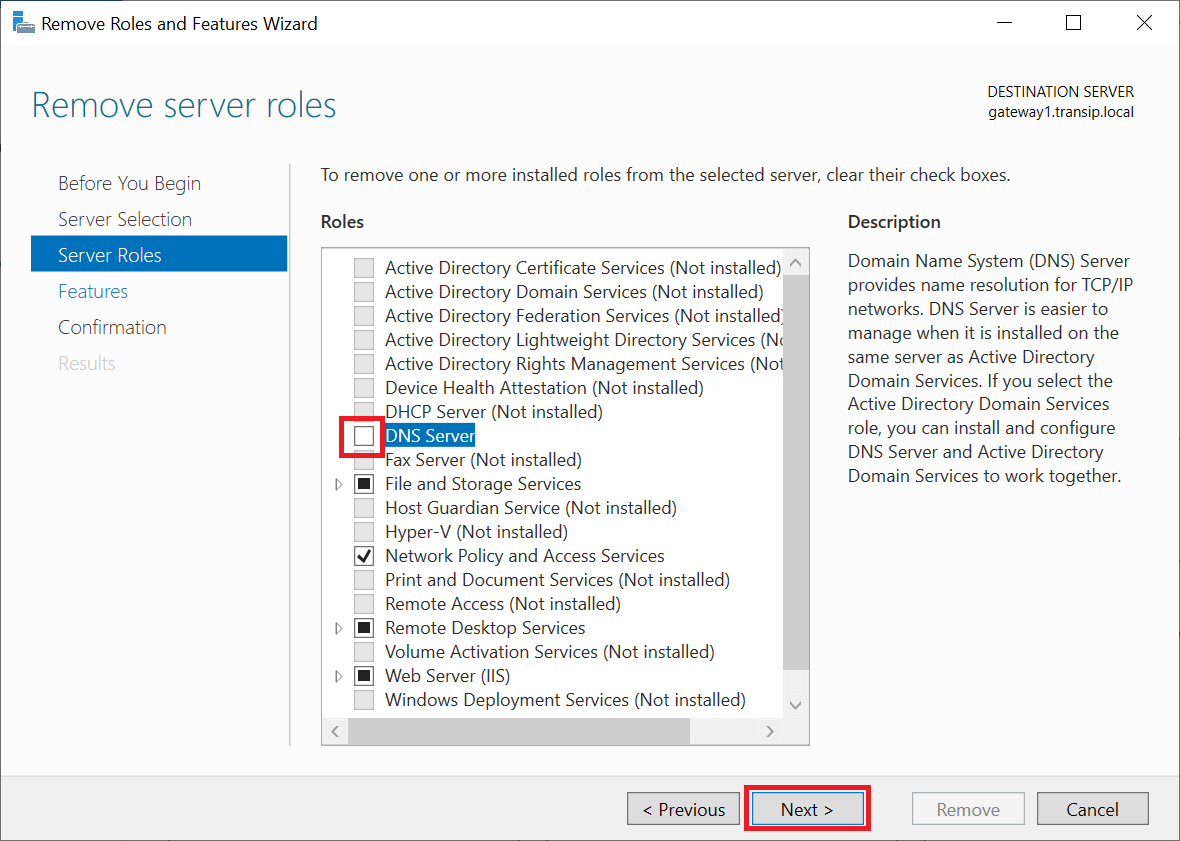
While Windows Server 2025 is a hypothetical future release, the process of removing a Windows Server operating system is a common task for system administrators. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to removing a Windows Server installation, covering various scenarios and potential challenges.
Understanding the Need for Removal
The need to remove a Windows Server installation can arise from several reasons:
- Hardware Replacement: Upgrading or replacing server hardware may necessitate a fresh installation of the operating system.
- Server Consolidation: Consolidating multiple servers onto fewer, more powerful machines may involve removing older servers.
- Operating System Upgrade: Moving to a newer version of Windows Server requires removing the previous version.
- End of Support: When a server reaches the end of its support lifecycle, it’s often advisable to remove it to minimize security risks.
- Server Retirement: If a server is no longer needed, it can be removed to free up resources and reduce maintenance costs.
Preparing for Removal
Before initiating the removal process, it’s crucial to take the following steps:
- Backup: Create a complete backup of all data and configurations on the server. This includes system files, applications, user data, and any other critical information. A comprehensive backup is essential for recovery in case of unforeseen issues during the removal process.
- Data Migration: If the server is being replaced or consolidated, migrate all data to the new server or storage location. This ensures data availability during and after the removal process.
- Application Migration: If applications are being moved, ensure their migration is completed successfully before removing the server. This step is critical to avoid disruption of services.
- User Notification: Inform users of the upcoming server removal and any potential service interruptions. This allows users to prepare and minimize disruptions to their workflow.
- Security Considerations: If the server is being removed due to security concerns, ensure appropriate measures are taken to prevent unauthorized access to data during the removal process. This may involve disabling remote access, changing passwords, and applying security patches.
Removal Methods
There are two primary methods for removing a Windows Server installation:
- Using the Windows Server Installation Media: This method involves booting the server from the Windows Server installation media and selecting the "Repair Your Computer" option. This option allows you to access a recovery environment where you can choose to reinstall the operating system or perform a clean installation.
- Using the Command Prompt: This method requires booting the server into the recovery environment and using the command prompt to execute the "format" command. This command will format the hard drive, effectively removing the operating system and all data.
Specific Scenarios
The removal process may differ slightly depending on the specific scenario:
- Removing a Server with Active Directory: Removing a server that is part of an Active Directory domain requires special care to avoid disrupting the domain. This process may involve transferring roles to another server, removing the server from the domain, and finally, removing the operating system.
- Removing a Server with Virtual Machines: If the server hosts virtual machines, it’s crucial to migrate the virtual machines to a different server before removing the host server. This ensures the virtual machines remain operational during the removal process.
- Removing a Server with Shared Storage: If the server uses shared storage, it’s essential to ensure that the storage is properly disconnected from the server before removing the operating system.
Troubleshooting and Recovery
During the removal process, you may encounter errors or unexpected behavior. In such cases, it’s crucial to troubleshoot the issue and take appropriate steps to recover the server.
- Error Messages: Pay close attention to error messages and consult relevant documentation or online resources for solutions.
- Recovery Options: If the removal process fails, use the recovery options provided by the Windows Server installation media or the command prompt to restore the server to a previous state.
- Contact Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue independently, contact Microsoft support for assistance.
FAQs
Q: Can I simply delete the Windows Server folder to remove the operating system?
A: No, deleting the Windows Server folder will not completely remove the operating system. It will only remove some files and may leave the system in an unstable state. It is essential to use the appropriate removal methods described above.
Q: What happens to my data when I remove the operating system?
A: Removing the operating system will erase all data on the hard drive. Therefore, it is crucial to back up all data before proceeding with the removal process.
Q: Is there a way to remove the operating system without losing my data?
A: It is generally not possible to remove the operating system without losing data. However, you can use data migration techniques to move data to another location before removing the operating system.
Q: What happens if I remove the server from the domain before removing the operating system?
A: Removing the server from the domain before removing the operating system may cause issues with the domain and other servers. It is generally recommended to remove the server from the domain after removing the operating system.
Tips
- Plan Carefully: Thorough planning is essential for a successful removal process. Consider all potential issues and develop a detailed plan before starting.
- Document the Process: Document all steps taken during the removal process. This will be helpful for troubleshooting and future reference.
- Test Before Production: If possible, test the removal process on a non-production server before implementing it on a production server.
- Seek Expert Help: If you are not comfortable performing the removal process yourself, seek help from a qualified IT professional.
Conclusion
Removing a Windows Server installation requires careful planning, execution, and troubleshooting. By following the steps outlined in this guide, system administrators can safely and effectively remove Windows Server installations, ensuring data integrity and minimal disruption to operations. Remember, a comprehensive understanding of the removal process, thorough preparation, and proper documentation are key to a successful outcome.

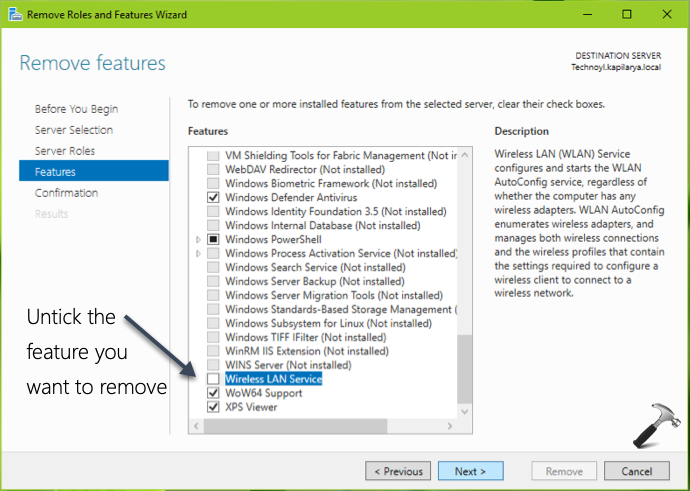
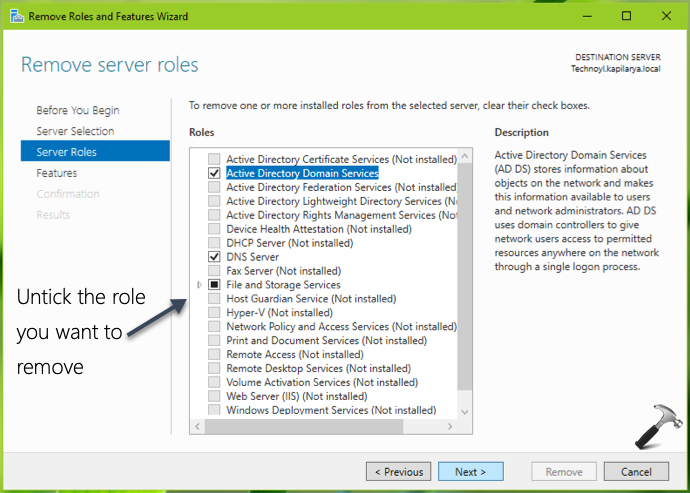


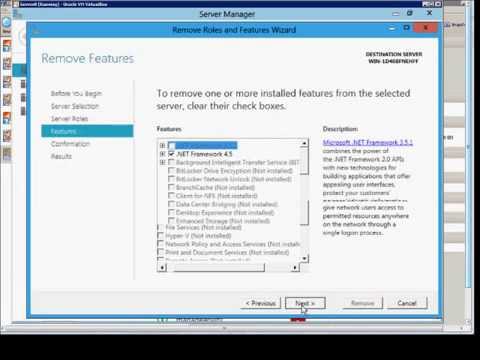
![[SOLVED] Issue with windows Server..removing ad server roles and features](https://content.spiceworksstatic.com/service.community/p/post_images/0000321486/5b6db77b/attached_image/Clipboard01.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Removing Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
