Understanding the Network Foundation of Active Directory in Windows Server 2025: A Deep Dive
Related Articles: Understanding the Network Foundation of Active Directory in Windows Server 2025: A Deep Dive
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Network Foundation of Active Directory in Windows Server 2025: A Deep Dive. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Network Foundation of Active Directory in Windows Server 2025: A Deep Dive

Active Directory (AD) is the cornerstone of any Windows Server-based network, serving as the central directory service for managing users, computers, and resources. While the specific ports used by AD are subject to change with each Windows Server release, understanding the underlying network communication is critical for network administrators and security professionals. This article delves into the fundamental network protocols and ports associated with Active Directory in Windows Server 2025, providing a comprehensive guide for network management and security considerations.
The Foundation of Active Directory Communication: TCP/IP and UDP
Active Directory relies heavily on the TCP/IP protocol suite for network communication. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) provides a reliable, connection-oriented data transfer mechanism, ensuring data integrity and order. UDP (User Datagram Protocol), on the other hand, offers a connectionless, less reliable but faster data transfer method. Understanding these protocols is crucial for configuring network firewalls and understanding potential communication issues.
Key Ports for Active Directory Operations
Active Directory leverages several critical ports for its core functionalities. While the specific ports may vary depending on the AD domain functional level and other factors, the following are essential for understanding AD network communication:
1. LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol):
- Port 389 (TCP/UDP): LDAP is the primary protocol used for querying and modifying data within Active Directory. It provides a standardized mechanism for accessing directory information, allowing applications and users to retrieve data about users, computers, groups, and other AD objects.
- Port 636 (TCP): LDAP over SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encrypts the communication between clients and the AD server, enhancing security and confidentiality.
2. Kerberos Authentication:
- Port 88 (TCP/UDP): Kerberos is a robust authentication protocol used by Active Directory. It provides a secure way for clients to authenticate to AD servers and access network resources. Port 88 is used for Kerberos authentication requests and responses.
3. DNS (Domain Name System):
- Port 53 (TCP/UDP): DNS is essential for resolving domain names to IP addresses. Active Directory relies heavily on DNS for name resolution, allowing clients to locate and connect to domain controllers.
4. RPC (Remote Procedure Call):
- Port 135 (TCP/UDP): RPC allows applications to communicate with remote services. Active Directory uses RPC for various functions, including domain controller location, group policy processing, and replication.
5. WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service):
- Port 42 (UDP): WINS is a legacy name resolution service, used primarily for backwards compatibility. Active Directory relies on DNS as its primary name resolution system, but WINS support may still be required in older environments.
6. Other Important Ports:
- Port 445 (TCP/UDP): SMB (Server Message Block) is used for file and printer sharing. Active Directory uses SMB for several functions, including administrative tasks and group policy processing.
- Port 139 (TCP/UDP): NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) is a legacy protocol for name resolution. Active Directory uses NetBT for backwards compatibility, but it is not as widely used as DNS.
Beyond the Ports: Understanding Network Communication
While understanding the specific ports used by Active Directory is crucial, it is equally important to grasp the broader network communication patterns. Active Directory relies on a complex network infrastructure, with multiple servers and clients interacting through these ports.
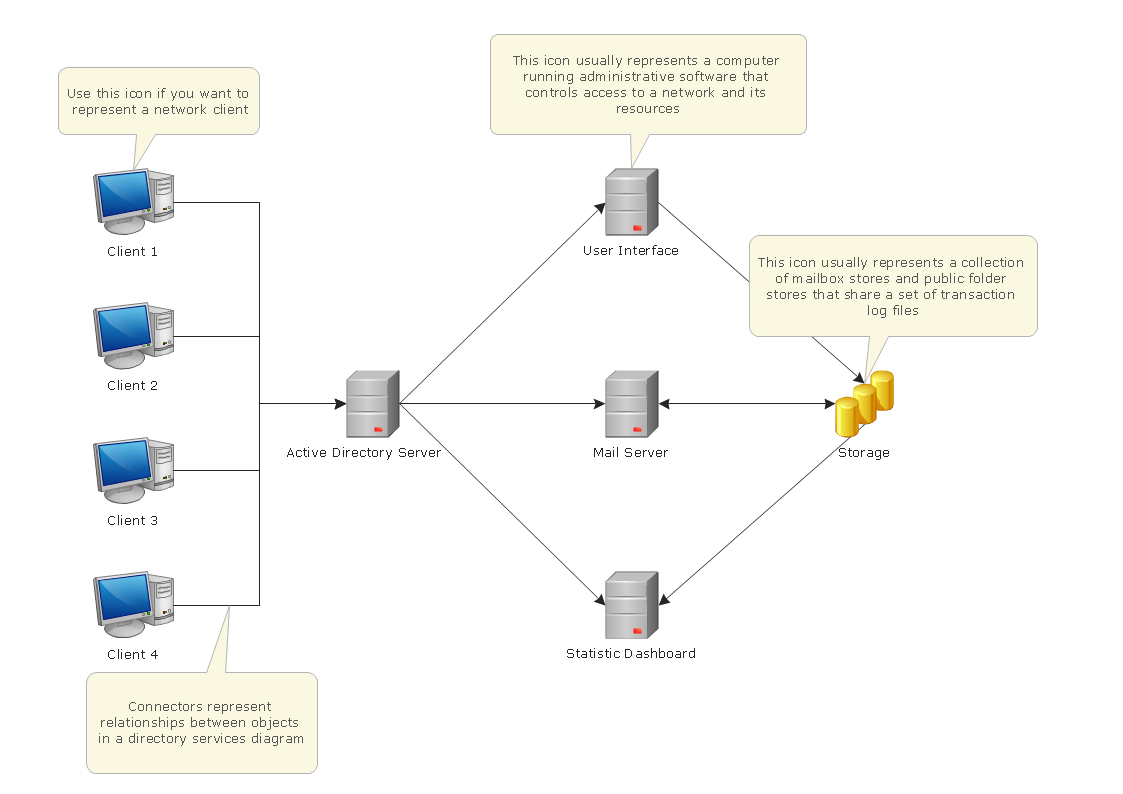
1. Domain Controllers and Clients:
Clients (computers and users) communicate with domain controllers to authenticate, access resources, and perform administrative tasks. This communication typically involves LDAP, Kerberos, DNS, and RPC protocols.
2. Domain Controller Replication:
Domain controllers replicate data between each other, ensuring data consistency across the entire Active Directory forest. This replication process utilizes various protocols, including LDAP, RPC, and SMB.
3. Group Policy Processing:
Group Policy is a powerful mechanism for managing user and computer settings. Domain controllers use RPC and SMB to communicate with clients and apply group policy settings.
4. Security Considerations:
Proper network security is paramount for protecting Active Directory. Network firewalls should be configured to allow only necessary traffic to and from AD servers. Secure protocols like LDAP over SSL/TLS should be used to encrypt communication.
Benefits of Understanding Active Directory Ports
Comprehending the network protocols and ports used by Active Directory provides several advantages:
- Network Troubleshooting: Identifying network communication issues can be streamlined by understanding the relevant ports and protocols.
- Security Enhancement: Proper firewall configuration and secure protocol usage help protect Active Directory from unauthorized access and attacks.
- Optimized Network Performance: Understanding communication patterns allows for network optimization and resource allocation.
FAQs on Active Directory Ports
1. What is the difference between TCP and UDP ports?
TCP ports provide a reliable, connection-oriented communication channel, ensuring data integrity and order. UDP ports offer a faster, connectionless method, but data integrity is not guaranteed.
2. How do I determine the specific ports used by Active Directory in my environment?
The specific ports used by Active Directory can vary depending on the domain functional level, configuration, and other factors. You can use tools like Netstat and Portqry to identify the ports used by Active Directory services.
3. Why is it important to secure Active Directory ports?
Securing Active Directory ports is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. Firewalls should be configured to block unnecessary traffic to and from AD servers.
4. Can I change the default ports used by Active Directory?
It is generally not recommended to change the default ports used by Active Directory, as this can disrupt network communication and cause compatibility issues.
5. What are the best practices for managing Active Directory ports?
- Use secure protocols like LDAP over SSL/TLS.
- Configure firewalls to block unnecessary traffic.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Keep Active Directory services up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Tips for Managing Active Directory Ports
- Document Port Usage: Maintain a record of all ports used by Active Directory services.
- Use Port Scanning Tools: Periodically scan your network for open ports and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Divide your network into smaller segments to limit the impact of security breaches.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Use network monitoring tools to detect unusual traffic patterns.
Conclusion
Understanding the network protocols and ports used by Active Directory is fundamental for effective network management and security. By comprehending the communication patterns and implementing best practices, organizations can ensure secure, reliable, and efficient Active Directory operations. This knowledge empowers administrators to troubleshoot network issues, enhance security, and optimize network performance for a robust and secure IT infrastructure.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Network Foundation of Active Directory in Windows Server 2025: A Deep Dive. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
