Understanding the Power of Scalability: Exploring the Potential of Windows Server with Two Cores
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Scalability: Exploring the Potential of Windows Server with Two Cores
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Scalability: Exploring the Potential of Windows Server with Two Cores. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Scalability: Exploring the Potential of Windows Server with Two Cores

The evolution of technology has ushered in an era where data and its management are paramount. As organizations navigate the complex landscape of digital transformation, the need for robust and scalable server infrastructure becomes increasingly critical. Enter Windows Server, a powerful operating system that empowers businesses of all sizes to manage their data and applications efficiently.
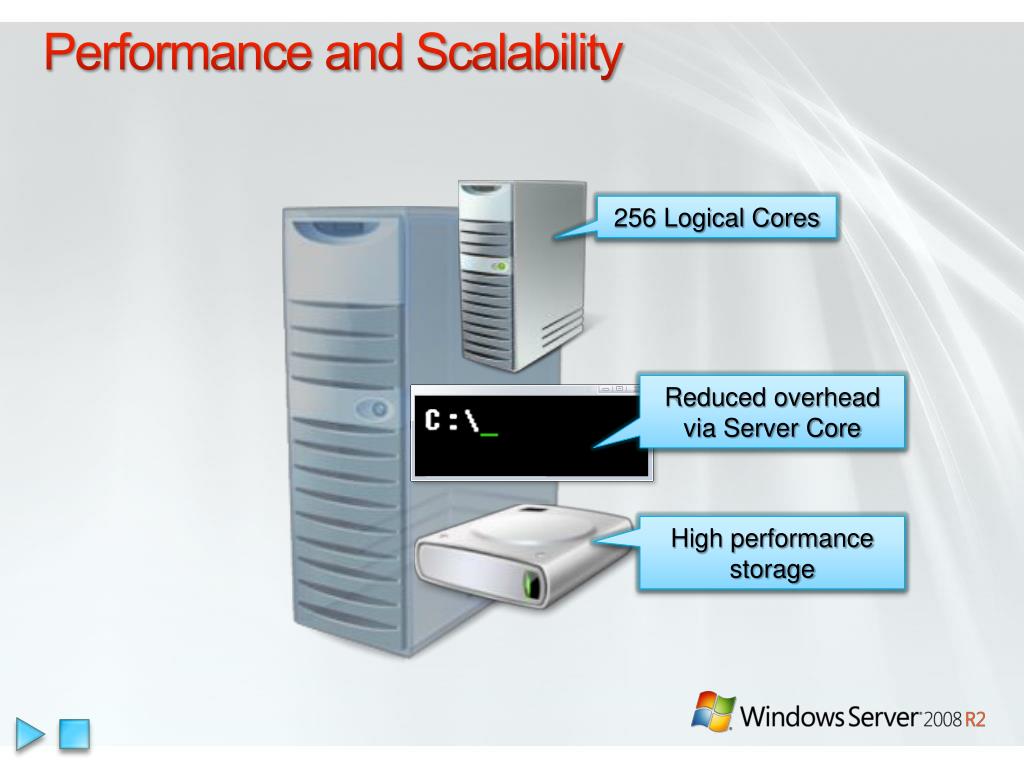
While Windows Server offers various configurations, one specific configuration stands out for its ability to balance performance and cost-effectiveness: a server equipped with two processing cores. This configuration, often referred to as a "two-core server," provides an ideal balance of processing power and resource utilization, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications and workloads.
The Power of Two: Unlocking the Potential of a Two-Core Server
At the heart of a server lies its processor, the engine that drives all operations. A two-core server, equipped with two processing units, can effectively handle multiple tasks simultaneously. This parallel processing capability significantly enhances performance, enabling servers to manage demanding applications and processes with greater efficiency.
Benefits of a Two-Core Server Configuration:
- Enhanced Performance: The two cores work in tandem, allowing the server to handle multiple tasks concurrently. This results in faster processing times, quicker response times, and a smoother user experience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to servers with more cores, a two-core server offers a more affordable option without compromising on essential functionality. This makes it an attractive choice for organizations with budget constraints.
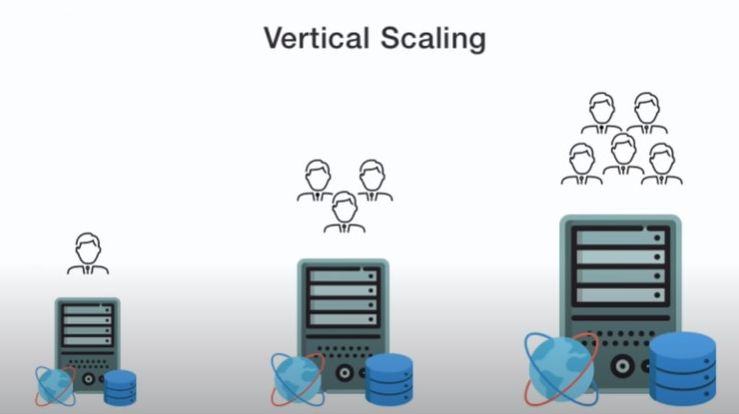
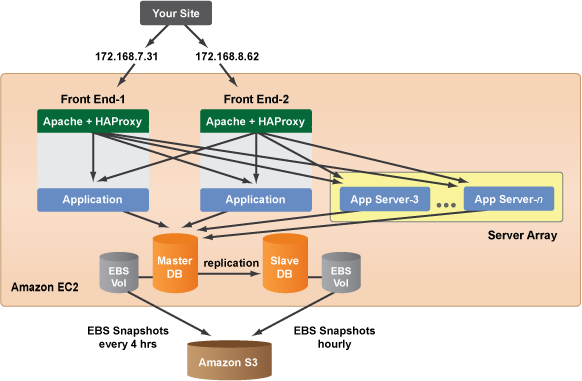
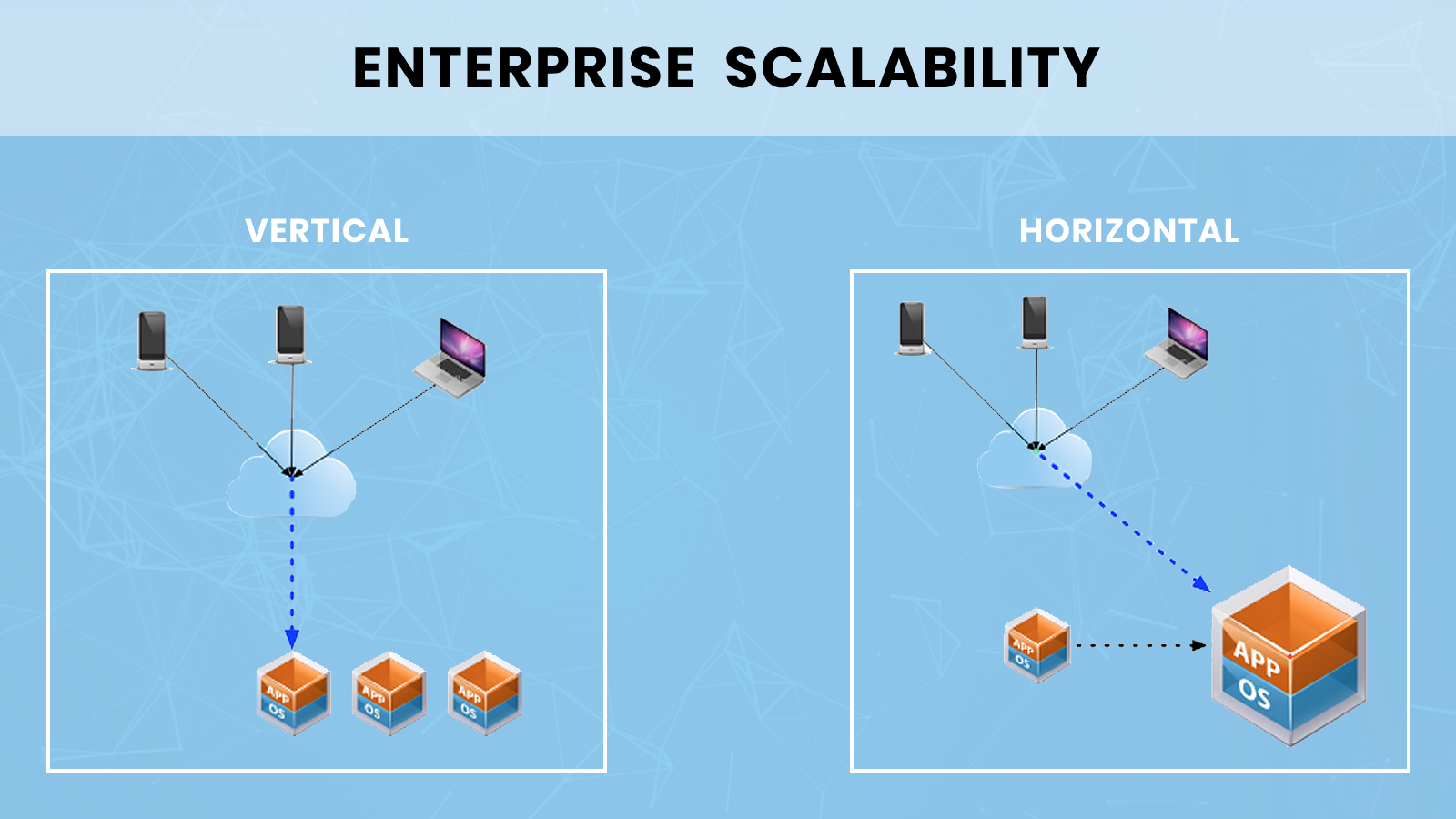
- Scalability: While a two-core server may not be suitable for the most demanding workloads, it provides a solid foundation for scaling up as your needs grow. You can easily add more resources, including additional cores, to accommodate increasing demands.
- Versatility: Two-core servers can effectively handle a wide range of applications, from basic file sharing and web hosting to more demanding tasks like database management and virtual machine hosting.
Use Cases for a Two-Core Server:
- Small Businesses and Startups: A two-core server provides a cost-effective solution for managing basic operations, including email, file sharing, and website hosting.
- Remote Offices and Branch Locations: Two-core servers are ideal for smaller offices or remote branches that require basic server functionality without the need for extensive resources.
- Development and Testing Environments: Developers and testers often utilize two-core servers for setting up and managing development and testing environments.
- Specialized Applications: Certain applications, such as media streaming or web server applications, can benefit from the balanced performance and resource management of a two-core server.
Understanding the Specifications:
While the term "two-core server" provides a general understanding of the configuration, it’s crucial to delve deeper into the specific specifications to understand the server’s true capabilities.
Key factors to consider:
- Processor Type: The type of processor (e.g., Intel Core i5, AMD Ryzen 3) will significantly impact performance.
- Clock Speed: The speed at which the processor operates, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how quickly the server can process information.
- Memory (RAM): The amount of RAM available directly impacts the server’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Storage: The type and capacity of the storage solution will influence the server’s data storage and retrieval capabilities.
Choosing the Right Two-Core Server:
Selecting the right two-core server for your specific needs involves careful consideration of your current and future requirements.
Factors to consider:
- Workload: Analyze the type and volume of tasks the server will handle to determine the necessary processing power.
- Budget: Establish a budget and explore servers within that range.
- Scalability: Consider your future needs and ensure the server can be easily scaled up as your requirements grow.
- Support and Maintenance: Evaluate the level of support and maintenance provided by the vendor or service provider.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Two-Core Servers:
Q: Are two-core servers suitable for demanding applications?
A: While two-core servers can handle a wide range of applications, they may not be suitable for extremely demanding workloads that require significant processing power. For such scenarios, servers with more cores or higher-performance processors might be necessary.
Q: Can I upgrade a two-core server to accommodate future growth?
A: Yes, many two-core servers offer upgrade options. You can typically upgrade the RAM, storage, and even the processor to meet evolving requirements.
Q: What are the advantages of using a two-core server over a single-core server?
A: A two-core server offers significant advantages over a single-core server, including:
- Increased performance: The ability to handle multiple tasks concurrently leads to faster processing times and improved responsiveness.
- Improved resource utilization: The two cores can share the workload, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing bottlenecks.
- Enhanced stability: A two-core server can handle unexpected spikes in demand more effectively, ensuring greater stability and reliability.
Q: How can I monitor the performance of a two-core server?
A: Most operating systems, including Windows Server, provide built-in monitoring tools that allow you to track key performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk activity. You can also use third-party monitoring software for more comprehensive insights.
Tips for Optimizing a Two-Core Server:
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance tasks, such as software updates, antivirus scans, and disk cleanup, to ensure optimal performance.
- Resource Management: Monitor resource usage and identify potential bottlenecks. You can adjust settings or optimize applications to improve performance.
- Virtualization: Consider using virtualization to create multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization.
- Cloud Integration: Explore cloud-based solutions for tasks that require significant processing power or storage capacity, allowing you to leverage external resources when needed.
Conclusion:
A two-core server offers a compelling balance of performance and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications and workloads. By understanding the benefits, use cases, and key considerations associated with this configuration, organizations can make informed decisions about their server infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and scalability for their evolving needs.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Scalability: Exploring the Potential of Windows Server with Two Cores. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
