Understanding the Power of Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor
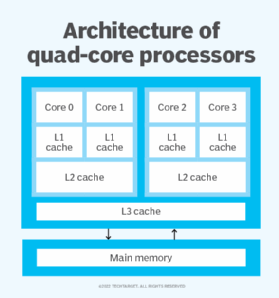
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and with it, the demands on server infrastructure are growing exponentially. Organizations of all sizes are seeking robust, reliable, and efficient solutions to manage their data, applications, and services. In this context, understanding the capabilities of a Windows Server equipped with a 4-core processor becomes critical.
This article delves into the advantages of a 4-core processor within the Windows Server environment, exploring its impact on performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It will also address common questions surrounding this configuration, provide practical tips for optimal utilization, and conclude with a clear understanding of its role in the modern IT landscape.
The Benefits of a 4-Core Processor in Windows Server
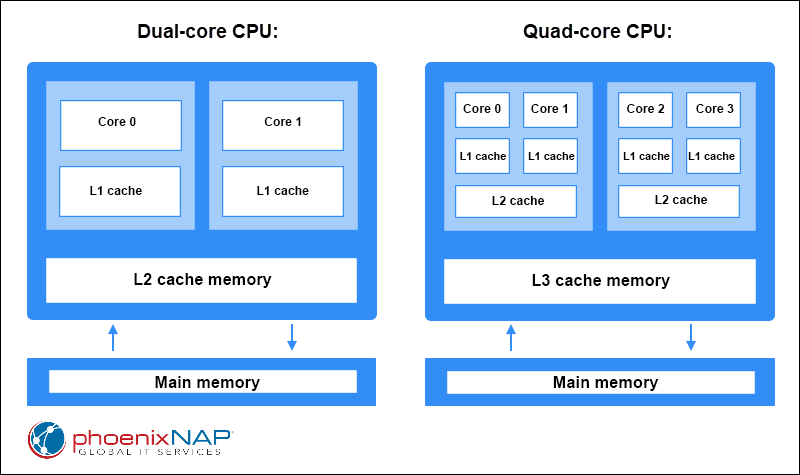
A 4-core processor offers a significant advantage over single-core or dual-core processors in a Windows Server environment. The benefits stem from its ability to execute multiple tasks concurrently, enhancing performance and efficiency.
-
Increased Processing Power: A 4-core processor provides a substantial boost in processing power, enabling the server to handle demanding workloads with greater efficiency. This translates to faster application execution, improved response times, and smoother user experiences.
-
Enhanced Multitasking: The ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously is a key advantage of a multi-core processor. With four cores, the server can effectively manage various processes, such as running virtual machines, hosting web applications, or managing databases, without compromising performance.
-
Improved Scalability: A 4-core processor provides a solid foundation for scalability. As the workload grows, the server can handle the increased demands with minimal performance degradation. This allows for smooth expansion of services and applications without requiring significant hardware upgrades.
-
Reduced Latency: The ability to process tasks concurrently minimizes latency, leading to faster response times and improved user experience. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time processing, such as online gaming or financial trading platforms.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: While a 4-core processor may have a slightly higher initial cost compared to lower core configurations, it offers long-term cost savings. The increased performance and efficiency translate to lower energy consumption and reduced maintenance costs.
Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the typical use cases for a Windows Server with a 4-core processor?
A Windows Server with a 4-core processor is well-suited for a wide range of use cases, including:
-
Small and Medium Businesses (SMB): For SMBs, a 4-core server can efficiently manage core business applications, file storage, and email services.
-
Web Hosting: Hosting websites and web applications, particularly those with moderate traffic, is a common application for a 4-core server.
-
Virtualization: Hosting multiple virtual machines on a single server is a cost-effective way to optimize resource utilization. A 4-core processor provides sufficient power for running multiple virtual machines simultaneously.
-
Database Management: Managing databases for applications and websites can be efficiently handled by a 4-core server, providing adequate processing power and memory for database operations.
2. How does a 4-core processor affect the overall performance of a Windows Server?
A 4-core processor significantly improves the overall performance of a Windows Server by:
-
Faster Application Execution: Applications run noticeably faster, leading to improved user experiences and increased productivity.
-
Reduced Response Times: The server responds quickly to user requests, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing downtime.
-
Enhanced Multitasking: The server can handle multiple tasks simultaneously without compromising performance, allowing for efficient resource utilization.
3. Is a 4-core processor sufficient for all workloads?
While a 4-core processor offers significant performance advantages, it may not be sufficient for all workloads. For highly demanding applications like large-scale virtualization or complex scientific simulations, a server with more cores or a higher-performance processor might be necessary.
4. What are the key factors to consider when choosing a 4-core processor for a Windows Server?
When choosing a 4-core processor for a Windows Server, consider the following factors:
-
Clock Speed: A higher clock speed generally translates to faster processing speeds, but other factors like cache size and instruction set also play a role.
-
Cache Size: Larger cache sizes allow the processor to store more frequently used data, leading to faster access times.
-
Instruction Set: The instruction set determines the types of operations the processor can perform. A more comprehensive instruction set can lead to better performance for certain tasks.
-
Power Consumption: Consider the power consumption of the processor, especially if energy efficiency is a concern.
5. What are the benefits of using a 4-core processor in a virtualized environment?
A 4-core processor is ideal for virtualization as it allows for:
-
Running Multiple Virtual Machines: A 4-core processor can efficiently host multiple virtual machines, providing each with sufficient processing power.
-
Improved Resource Utilization: Virtualization allows for efficient utilization of hardware resources, minimizing idle time and maximizing performance.
-
Enhanced Flexibility: Virtualization provides flexibility in allocating resources, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on workload changes.
Tips for Optimizing a Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor
-
Enable Hyper-Threading: Hyper-threading allows a single processor core to handle multiple threads simultaneously, further boosting performance.
-
Optimize Memory Usage: Ensure sufficient RAM is available to support the server’s workload.
-
Configure Processor Affinity: Assign specific processes to specific cores to optimize performance for specific applications.
-
Monitor Resource Utilization: Regularly monitor processor usage, memory usage, and disk activity to identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
-
Implement Regular Maintenance: Perform regular updates and security patches to ensure optimal performance and system stability.
Conclusion
A Windows Server equipped with a 4-core processor offers a powerful and cost-effective solution for a wide range of business needs. Its ability to handle demanding workloads, manage multiple tasks concurrently, and provide a solid foundation for scalability makes it an ideal choice for businesses seeking to enhance their IT infrastructure. By understanding the benefits, addressing common questions, and implementing optimization tips, organizations can effectively utilize the power of a 4-core processor to drive efficiency, productivity, and growth.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Windows Server with a 4-Core Processor. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
