Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on Core-Based Licensing
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on Core-Based Licensing
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on Core-Based Licensing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on Core-Based Licensing

The landscape of server operating systems is constantly evolving, with Microsoft’s Windows Server at the forefront. As technology advances, so too do the licensing models that govern its use. One prominent shift has been the move towards core-based licensing, a method that has significant implications for organizations of all sizes. This article delves into the nuances of core-based licensing, specifically focusing on the considerations surrounding a Windows Server license with a two-core configuration.
Core-Based Licensing: A Shift in Paradigm
Prior to the introduction of core-based licensing, Windows Server licenses were primarily tied to the physical processor within a server. This meant that a single license allowed for a single processor, regardless of the number of cores within that processor. However, with the advent of multi-core processors, this approach became increasingly inefficient.
Core-based licensing, therefore, emerged as a more flexible and scalable solution. Instead of being tied to physical processors, licenses are now assigned based on the number of cores present within a server’s processors. This provides organizations with greater control over their licensing costs, allowing them to purchase licenses only for the cores they actually need.
The Two-Core License: A Cost-Effective Option
The two-core license model is particularly attractive for organizations with modest server requirements. It provides a cost-effective solution for servers that do not demand significant processing power, such as those used for file sharing, small-scale databases, or basic web hosting.
Key Considerations for Two-Core Licenses
While the two-core license offers an economical option, it’s crucial to carefully consider the following factors before making a decision:
- Server Requirements: The most important aspect is to accurately assess the workload your server will handle. A two-core configuration may be suitable for light workloads but may prove insufficient for demanding applications or high traffic scenarios.
- Scalability: Consider your future needs. If your workload is likely to grow, a two-core license might not provide sufficient headroom for expansion.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure that the software you intend to run on the server is compatible with the two-core license. Some applications might require more processing power than a two-core configuration can provide.
- Licensing Costs: While a two-core license is generally cost-effective, remember to factor in the cost of additional licenses if your needs grow beyond the initial two cores.
Benefits of Two-Core Licensing:
- Cost Savings: A two-core license is typically more affordable than licenses for servers with a higher core count, making it a budget-friendly option for organizations with limited resources.
- Simplified Management: Managing a server with a smaller number of cores can be simpler and more efficient.
- Flexibility: If your needs change in the future, you can easily upgrade to a license with more cores.
FAQs about Two-Core Windows Server Licenses:
Q: Can I use a two-core license on a server with more than two cores?
A: No, you cannot. A two-core license is only valid for servers with a maximum of two cores. To utilize a server with more cores, you will need to purchase additional licenses.
Q: How many virtual machines can I run with a two-core license?
A: The number of virtual machines you can run depends on the specific software you are using and the resources available. However, it’s essential to note that a two-core license will limit the overall processing power available for your virtual machines.
Q: What happens if my workload exceeds the capabilities of a two-core license?
A: If your workload exceeds the capacity of a two-core license, you will experience performance degradation, such as slower response times and application crashes. You may need to upgrade to a license with more cores to address these issues.
Tips for Optimizing Two-Core Windows Server Licenses:
- Optimize Server Configuration: Ensure that your server is properly configured to maximize performance. This includes disabling unnecessary services, optimizing memory usage, and ensuring that the operating system is up to date.
- Monitor Server Performance: Regularly monitor your server’s performance to identify any bottlenecks or potential issues. This will help you to proactively address problems before they impact your applications.
- Consider Virtualization: If you need to run multiple applications on a single server, virtualization can be a cost-effective solution.
Conclusion:
A two-core Windows Server license can be a cost-effective option for organizations with modest server requirements. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider your workload, scalability needs, and software compatibility before making a decision. By understanding the nuances of core-based licensing and diligently assessing your needs, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your organization’s specific requirements and budget.

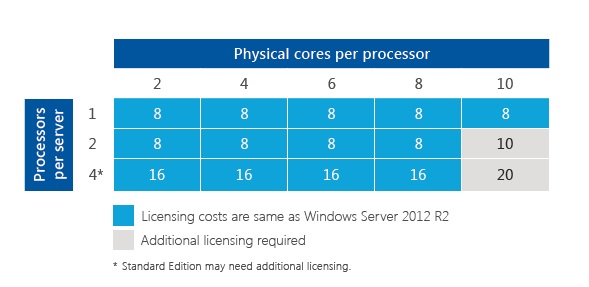


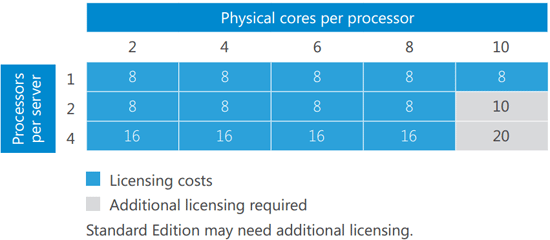

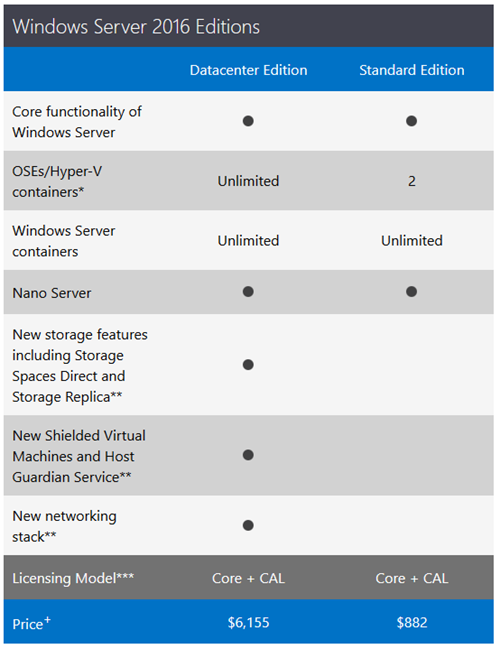
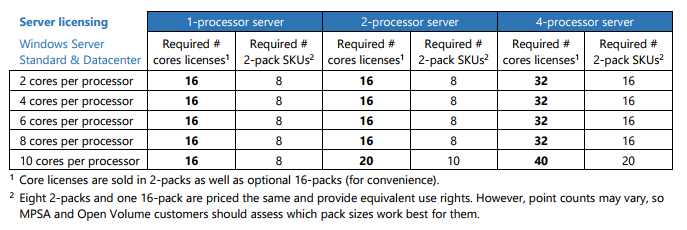
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on Core-Based Licensing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
