WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server
Related Articles: WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server
- 2 Introduction
- 3 WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server
- 3.1 Understanding WebDAV: A Deeper Dive
- 3.2 Implementing WebDAV on Windows Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Advantages of WebDAV in a Windows Server Environment
- 3.4 WebDAV Applications: Real-World Scenarios
- 3.5 WebDAV and Security: Best Practices
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Optimizing WebDAV Performance
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server

WebDAV, short for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning, is a powerful protocol that extends the functionality of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to enable collaborative file sharing and management over the internet. It allows users to access, modify, and manage files on a remote server as if they were directly on their local machine, facilitating seamless collaboration and remote file management. This article will delve into the intricacies of WebDAV on Windows Server, exploring its features, advantages, and practical applications.
Understanding WebDAV: A Deeper Dive
WebDAV leverages the familiar HTTP protocol, utilizing standard web browsers and client applications for interaction. Its key strength lies in its ability to extend HTTP functionality to support remote file operations, including:
- File Creation and Deletion: WebDAV allows users to create new files and folders on a remote server, as well as delete existing ones.
- File Editing and Modification: Users can modify the contents of existing files on the server, making changes directly through their web browser or client applications.
- File Copying and Moving: WebDAV facilitates the movement of files between different locations, both within the server and between local machines and the server.
- File Locking and Versioning: To prevent simultaneous editing conflicts, WebDAV enables file locking, ensuring that only one user can modify a file at a time. It also supports versioning, allowing users to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
- Metadata Management: WebDAV enables manipulation of file metadata, including attributes like permissions, timestamps, and descriptions, allowing for enhanced organization and control.
Implementing WebDAV on Windows Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up WebDAV on Windows Server is a straightforward process, typically involving the following steps:
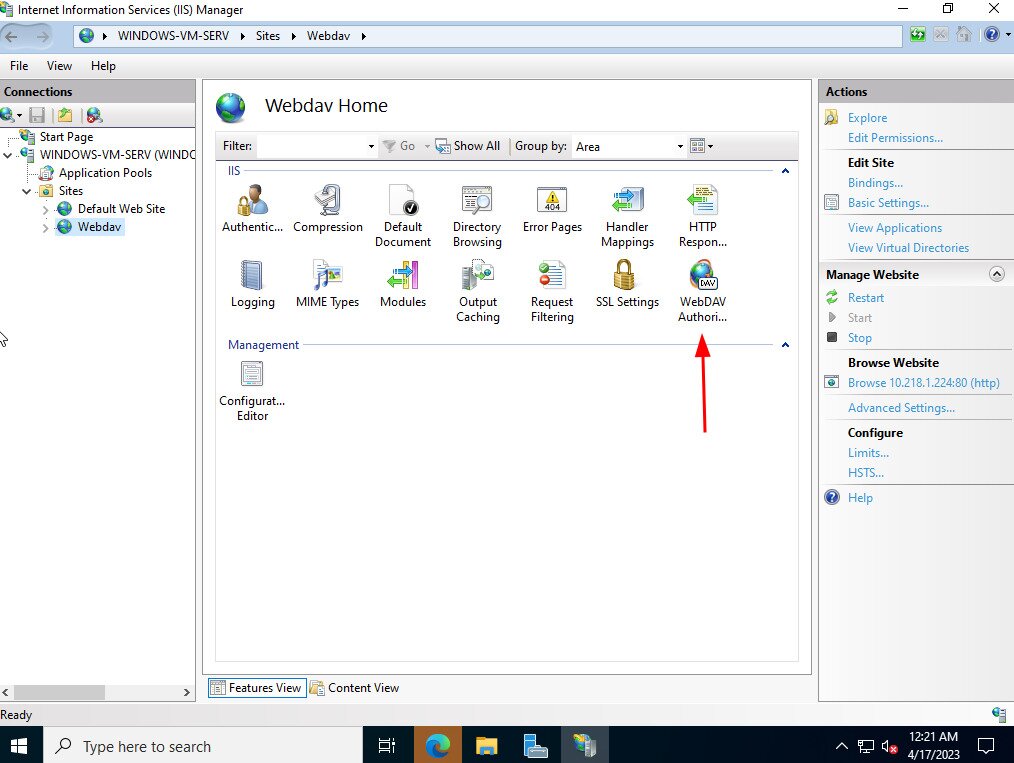
- Enabling WebDAV: Navigate to the "Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager" on the server and locate the website or virtual directory where you intend to enable WebDAV. Under the "WebDAV" section, enable the "WebDAV Publishing" option.
- Configuring Permissions: Define access permissions for users and groups, specifying which users can access specific files or folders and what actions they are permitted to perform.
- Configuring Authentication: Choose an authentication method, such as Basic Authentication, Digest Authentication, or Windows Authentication, to secure access to the shared files.
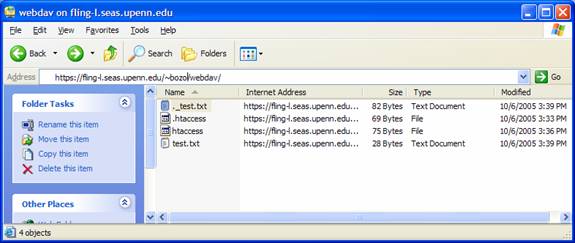
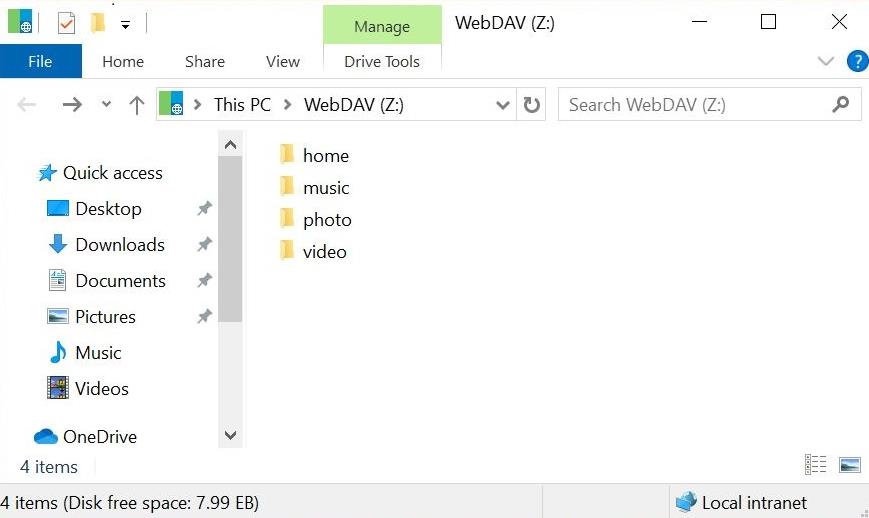
- Testing the Connection: Verify the WebDAV setup by accessing the shared files through a web browser or a client application. You can use the "http://server_name/webdav/folder" URL format to access the shared files.
Advantages of WebDAV in a Windows Server Environment
WebDAV offers numerous advantages for organizations and individuals utilizing Windows Server for file storage and sharing:
- Enhanced Collaboration: WebDAV allows multiple users to work on the same files concurrently, facilitating team projects and streamlining workflows.
- Remote Access: Users can access and manage files from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for physical presence at the server location.
- Simplified File Management: WebDAV provides a user-friendly interface for managing files on the server, allowing users to perform various operations through familiar web browsers or client applications.
- Increased Security: WebDAV supports various authentication methods, ensuring secure access to sensitive files and preventing unauthorized access.
- Cost-Effectiveness: WebDAV eliminates the need for expensive VPN connections or complex file sharing software, making it a cost-effective solution for remote file management.
WebDAV Applications: Real-World Scenarios
WebDAV finds applications in various scenarios, including:
- Document Management: WebDAV enables collaborative document editing and sharing within teams, allowing for seamless version control and efficient workflow management.
- Project Management: Project teams can use WebDAV to store, share, and manage project files, facilitating communication and collaboration among team members.
- Remote Backup and Recovery: WebDAV can be used for backing up critical data to a remote server, providing a secure and accessible backup solution.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): WebDAV is often used by CMS platforms to enable content authors to upload and manage website content from remote locations.
- Web-Based File Storage and Sharing: WebDAV can be integrated into web applications to provide users with secure file storage and sharing capabilities.
WebDAV and Security: Best Practices
Security is paramount when implementing WebDAV, as it involves sharing files over the internet. Here are some essential security best practices:
- Strong Authentication: Utilize strong authentication methods, such as Windows Authentication or Digest Authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to shared files.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement granular access control lists to define specific permissions for users and groups, limiting access to authorized individuals.
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Ensure secure communication by enabling SSL/TLS encryption to protect data transmitted over the internet.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities and ensure the security of your WebDAV setup.
- Firewall Configuration: Configure firewalls to restrict access to WebDAV services from unauthorized sources, further enhancing security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the advantages of using WebDAV over FTP?
A: WebDAV offers several advantages over FTP, including:
- Enhanced Functionality: WebDAV supports a wider range of file operations, including file locking, versioning, and metadata management, making it more versatile than FTP.
- Security: WebDAV supports more secure authentication methods, such as Digest Authentication and Windows Authentication, compared to FTP’s basic authentication.
- Integration with Web Browsers: WebDAV seamlessly integrates with web browsers, making it easier to access and manage files remotely.
Q: Is WebDAV compatible with all web browsers?
A: Most modern web browsers support WebDAV, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. However, older browsers might require additional plugins or extensions to enable WebDAV functionality.
Q: Can I use WebDAV with third-party file management applications?
A: Yes, many third-party file management applications, such as Filezilla and Cyberduck, support WebDAV, allowing for easy access and management of files on WebDAV-enabled servers.
Q: What are some popular WebDAV client applications?
A: Apart from web browsers, there are several popular WebDAV client applications available, including:
- Filezilla: A free and open-source FTP and WebDAV client with a user-friendly interface.
- Cyberduck: A cross-platform FTP, SFTP, and WebDAV client with advanced features and a modern design.
- Rclone: A command-line tool that supports various cloud storage services, including WebDAV.
Q: How can I troubleshoot WebDAV connectivity issues?
A: When troubleshooting WebDAV connectivity issues, consider the following:
- Firewall Configuration: Ensure that your firewall allows access to the WebDAV port (typically port 80 or 443).
- Authentication Credentials: Verify that you are using the correct username and password for authentication.
- WebDAV Configuration: Check your WebDAV configuration settings on the server, ensuring that the correct permissions and authentication methods are in place.
- Network Connectivity: Verify that your network connection is stable and that you can access other resources on the internet.
Tips for Optimizing WebDAV Performance
- Optimize Server Resources: Ensure that the server has sufficient resources, including CPU, memory, and disk space, to handle the workload of WebDAV traffic.
- Configure Caching: Enable caching on the server and client to reduce network traffic and improve performance.
- Use Compression: Configure WebDAV to compress data before transmission, reducing the amount of data transferred and improving performance.
- Minimize File Size: Optimize files for size, such as using compression techniques or removing unnecessary content, to reduce download times and improve performance.
- Limit Concurrent Connections: Configure the server to limit the number of concurrent connections to prevent overloading the server and ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
WebDAV, a powerful protocol built upon the foundation of HTTP, empowers Windows Server users to collaborate effectively, manage files remotely, and streamline workflows. Its ability to extend HTTP functionality to support file operations provides a user-friendly and secure means for accessing and managing files over the internet. By understanding its intricacies, implementing it correctly, and adhering to security best practices, organizations and individuals can leverage the full potential of WebDAV to enhance their file sharing and collaboration capabilities within a Windows Server environment.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into WebDAV: Enabling File Sharing and Collaboration on Windows Server. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
