Windows Server 2008 WebDAV: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Windows Server 2008 WebDAV: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Windows Server 2008 WebDAV: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows Server 2008 WebDAV: A Comprehensive Guide
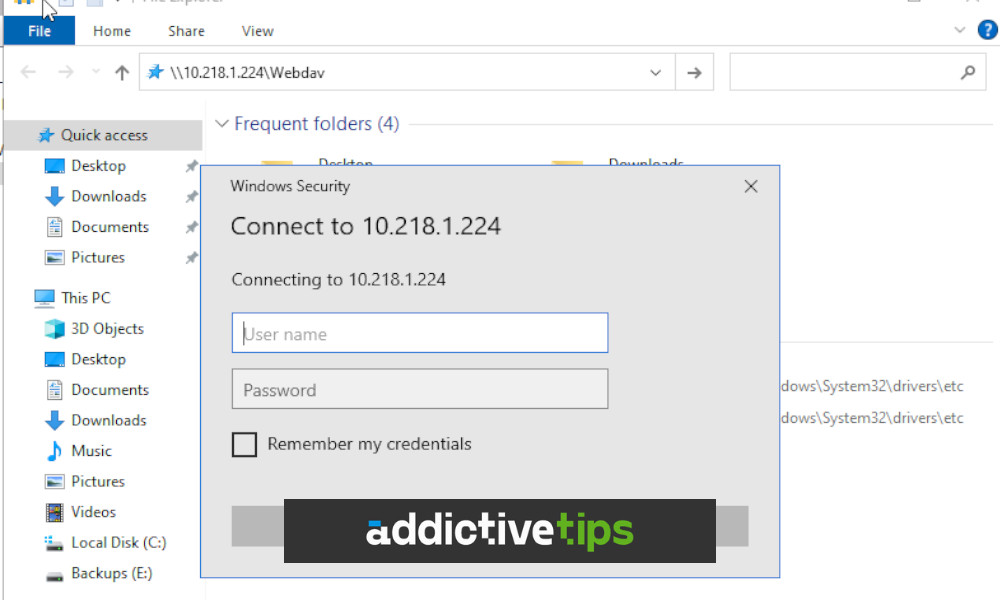
Windows Server 2008 introduced a powerful and versatile feature: Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). This protocol, built upon the foundation of HTTP, revolutionized file sharing and collaboration by extending the capabilities of standard web servers. WebDAV enabled users to access, manage, and modify files over the internet, transcending the limitations of traditional file transfer protocols. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of WebDAV on Windows Server 2008, exploring its functionalities, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding WebDAV: Beyond Simple File Transfers
At its core, WebDAV leverages the familiar HTTP protocol, enabling users to interact with files stored on a web server using standard web browsers. However, WebDAV goes beyond basic file retrieval, offering a robust set of functionalities that empower users to:
- Create, delete, and rename files and folders: Users can perform fundamental file management operations directly through their web browsers, eliminating the need for dedicated FTP clients.
- Upload and download files: WebDAV facilitates the transfer of files between client machines and the server, allowing users to easily share and access data.
- Lock and unlock files: This feature ensures data integrity by allowing users to lock files during editing, preventing accidental overwrites and ensuring consistent versions.
- Manage file permissions: Administrators can granularly control access to files and folders, ensuring data security and restricting unauthorized modifications.
- Track file versions: WebDAV enables the storage and retrieval of previous file versions, facilitating collaboration and version control.
Benefits of WebDAV on Windows Server 2008
WebDAV on Windows Server 2008 offers a compelling suite of advantages, making it a valuable tool for businesses and individuals alike:
- Simplified file sharing: WebDAV eliminates the need for complex file transfer protocols and dedicated software, streamlining file sharing across multiple platforms and locations.
- Enhanced collaboration: Users can work simultaneously on shared documents, track file versions, and seamlessly collaborate on projects without the need for physical proximity.
- Improved data accessibility: WebDAV allows users to access files from any location with an internet connection, promoting remote work and flexible collaboration.
- Centralized file management: WebDAV enables the consolidation of files on a central server, simplifying administration and ensuring data consistency.
- Increased security: WebDAV supports secure connections through HTTPS, safeguarding sensitive data during transfer and access.
Setting Up WebDAV on Windows Server 2008
Setting up WebDAV on Windows Server 2008 is a straightforward process involving the following steps:
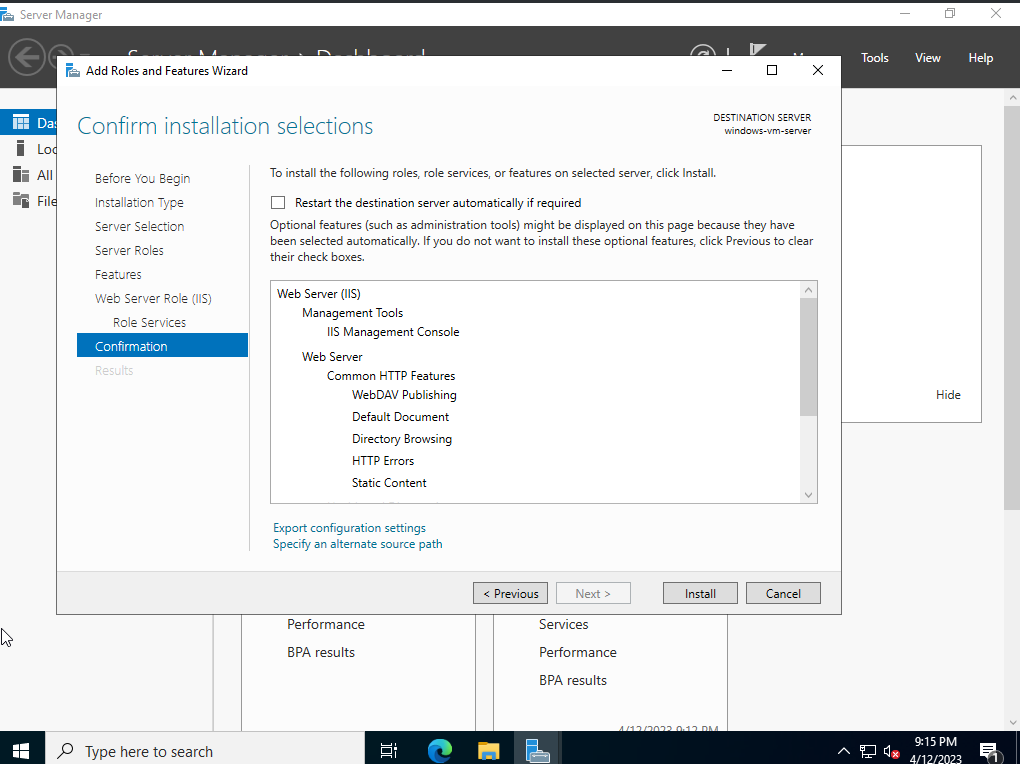
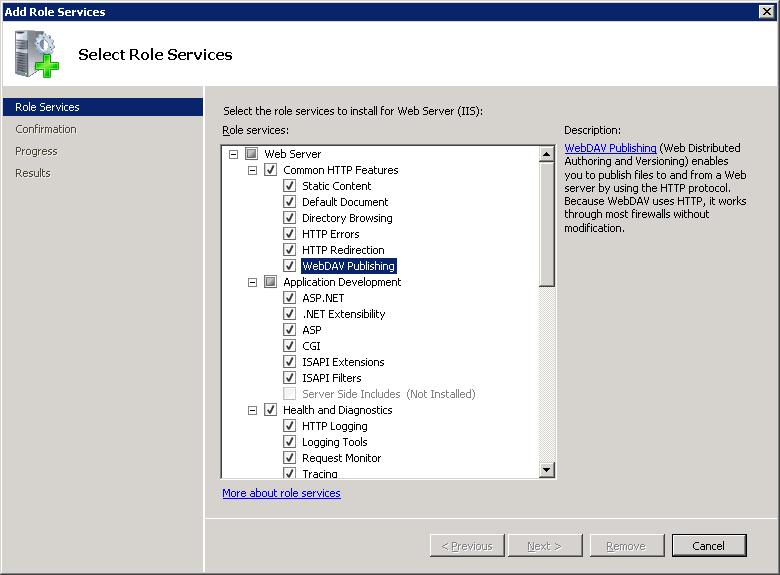
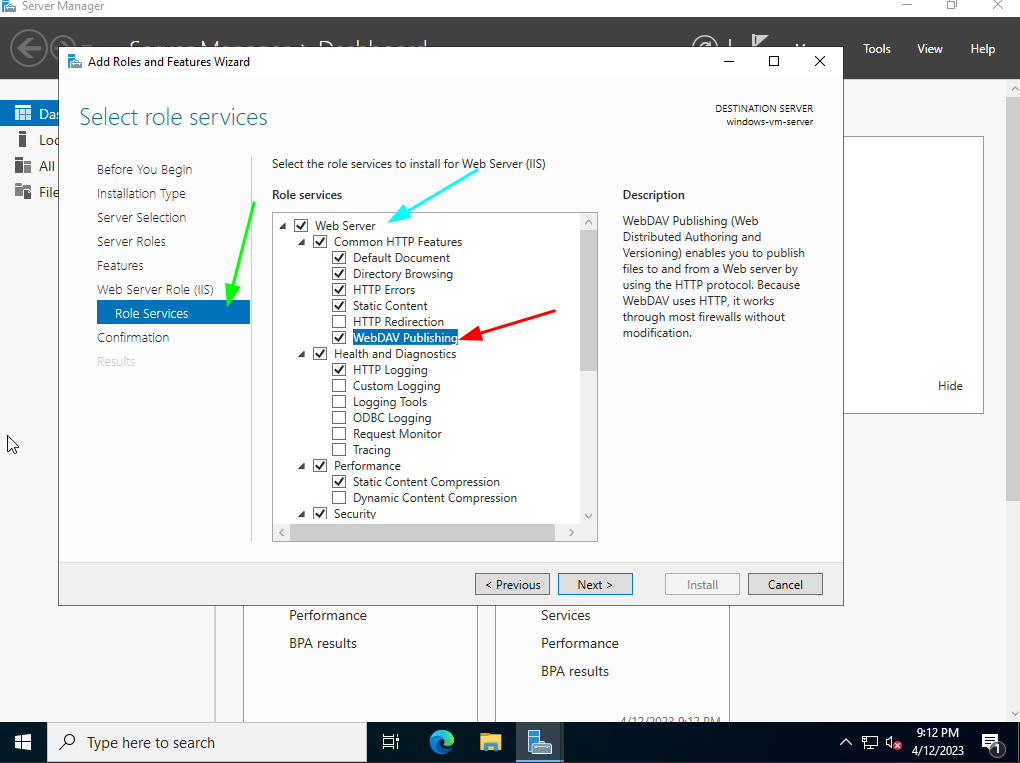
- Install IIS: Ensure that Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed on your server.
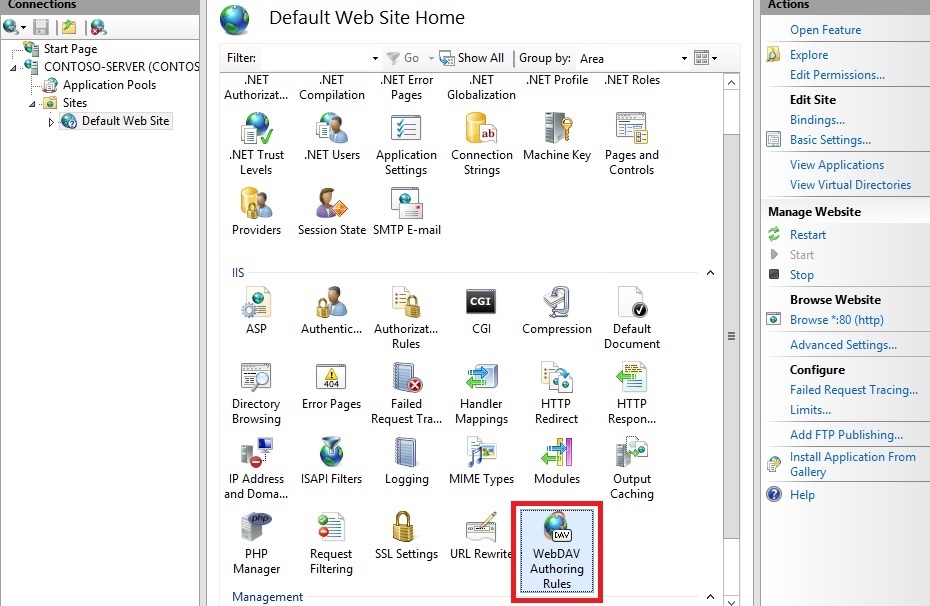
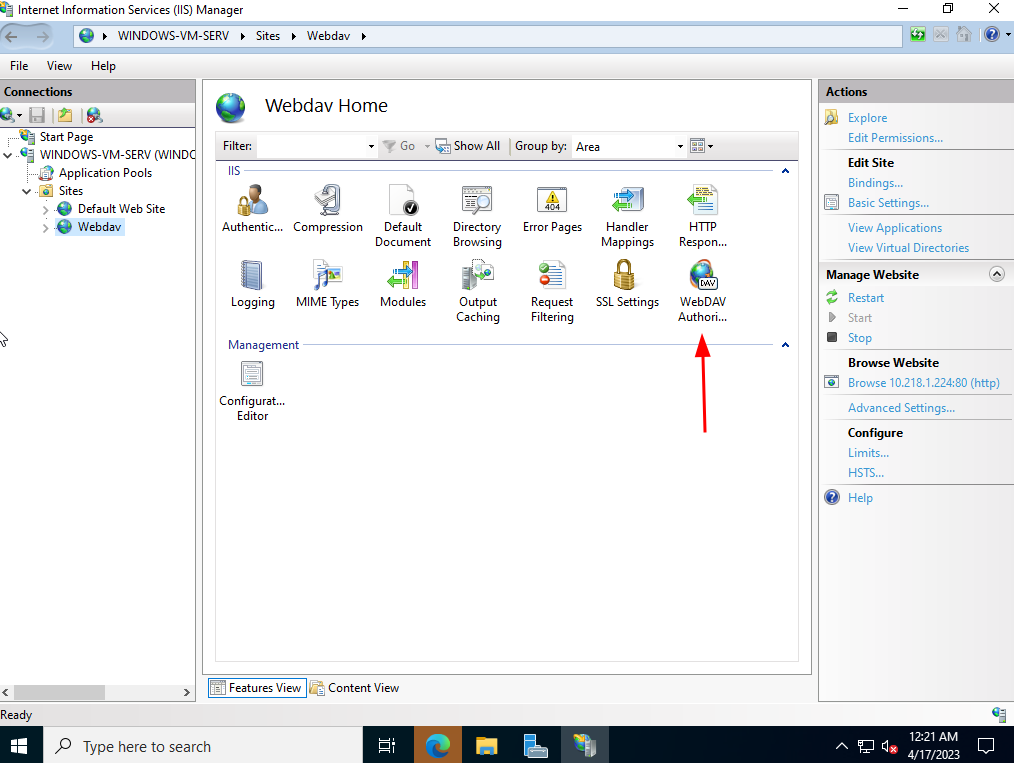
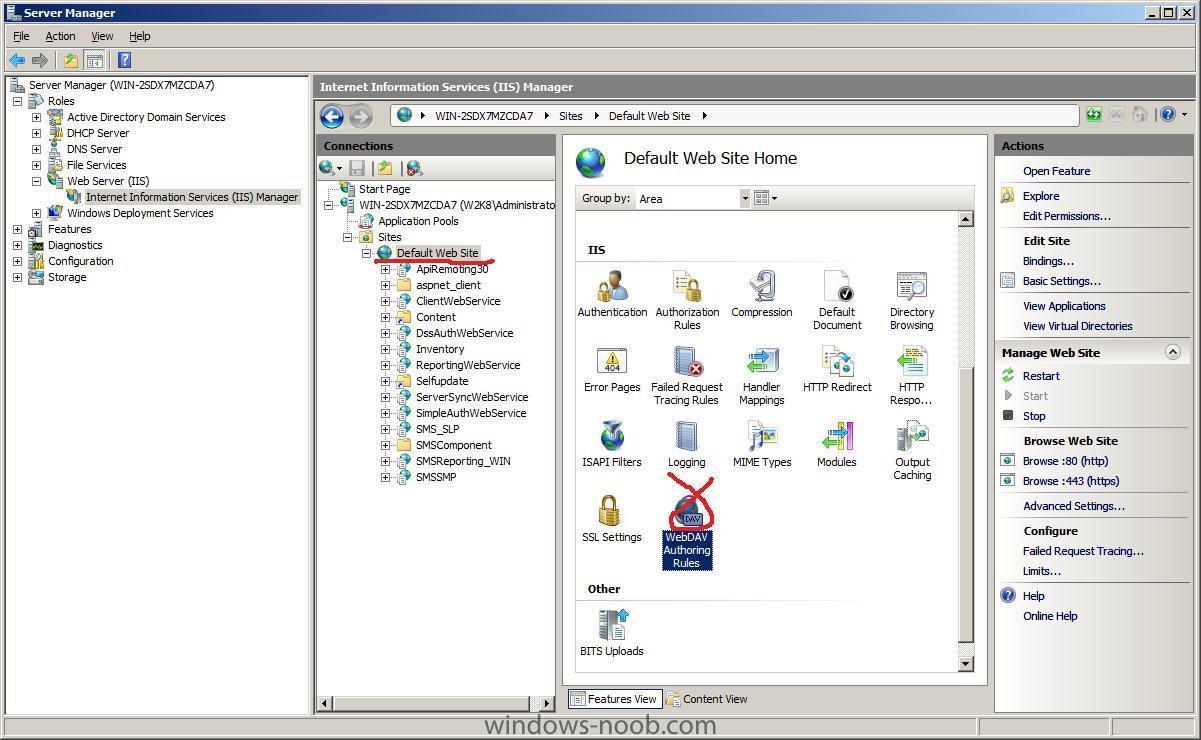
- Enable WebDAV: Navigate to the "IIS Manager" and select the desired website. Go to "WebDAV Authoring Rules" and enable WebDAV for the specified folder or website.
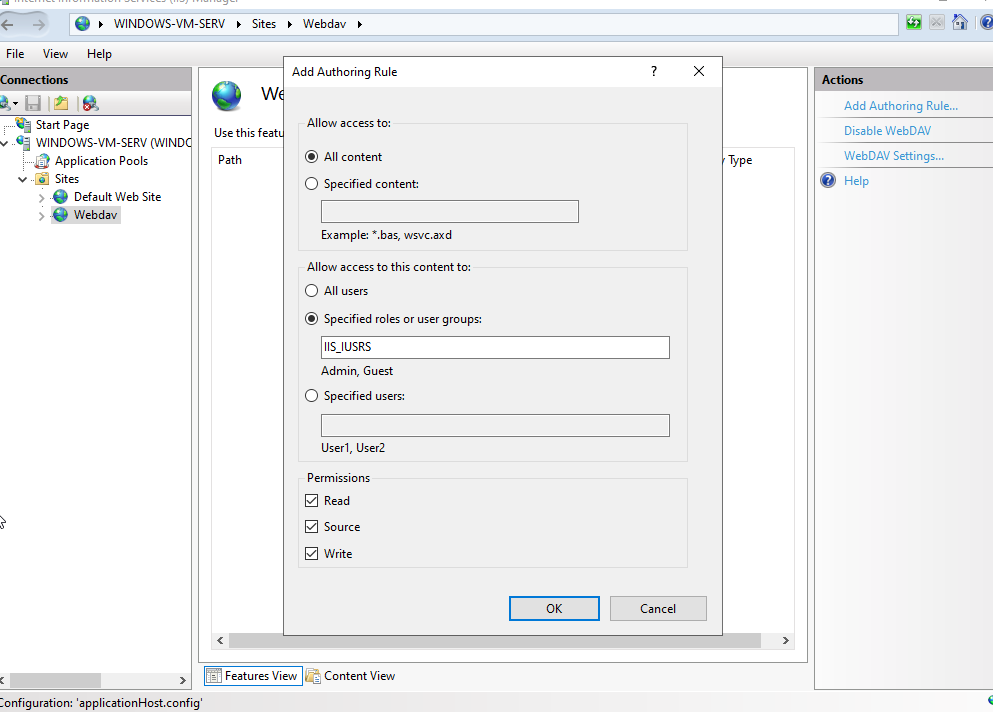
- Configure Permissions: Set appropriate permissions for users and groups to access and manage files within the designated WebDAV share.
- Test the Configuration: Access the WebDAV share through a web browser and verify that you can perform basic operations like file upload, download, and modification.
Practical Applications of WebDAV
WebDAV finds its place in a wide range of scenarios, serving as a versatile tool for diverse applications:
- Document collaboration: Teams can use WebDAV to share and edit documents, presentations, and spreadsheets, facilitating seamless collaboration on projects.
- Content management: WebDAV can be used to manage website content, allowing editors to upload, modify, and publish files directly from their web browsers.
- File backup and synchronization: WebDAV can be leveraged to automate file backups and synchronize data across multiple devices, ensuring data integrity and redundancy.
- Remote file access: WebDAV enables users to access files stored on a server from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and access to important documents.
- Web-based file sharing: WebDAV can be integrated into web applications, allowing users to upload and download files directly from their web browsers, enhancing the user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Windows Server 2008 WebDAV
Q: Is WebDAV compatible with all web browsers?
A: WebDAV is a standard protocol supported by most modern web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer. However, some older browsers might require plugins or extensions for full WebDAV functionality.
Q: How secure is WebDAV?
A: WebDAV itself is not inherently secure, but it can be implemented with HTTPS encryption for secure data transfer. It is essential to use HTTPS for all WebDAV interactions to protect sensitive data.
Q: Can I use WebDAV with other operating systems?
A: Yes, WebDAV is a cross-platform protocol, allowing users on Windows, macOS, Linux, and other operating systems to access and manage files on a WebDAV server.
Q: What are the limitations of WebDAV?
A: WebDAV is primarily designed for file sharing and collaboration, not for complex file management tasks. It might not be suitable for large file transfers or real-time collaboration on highly sensitive data.
Q: How can I troubleshoot WebDAV issues?
A: Common troubleshooting steps include verifying firewall settings, checking permissions, ensuring the server is running, and reviewing IIS logs for error messages.
Tips for Using WebDAV on Windows Server 2008
- Implement HTTPS: Always use HTTPS to secure data transmission and ensure data integrity.
- Configure permissions carefully: Grant only necessary access to users and groups to protect sensitive data.
- Monitor server logs: Regularly review server logs for potential issues and security threats.
- Use a reliable web browser: Ensure you are using a modern web browser that fully supports WebDAV functionality.
- Back up your data: Regularly back up your WebDAV share to prevent data loss.
Conclusion
Windows Server 2008 WebDAV provides a powerful and versatile solution for file sharing and collaboration. Its simplicity, compatibility, and security features make it an invaluable tool for businesses and individuals seeking to streamline file management, enhance collaboration, and increase data accessibility. By understanding its functionalities, benefits, and practical applications, users can leverage WebDAV to optimize their file sharing and collaboration workflows, ultimately boosting productivity and efficiency.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows Server 2008 WebDAV: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
